Original Map Of India
Bhārat Gaṇarājya | |
|---|---|
Motto: 'Satyameva Jayate'(Sanskrit) | |
Anthem: 'Jana Gana Mana'[2][3] 'Thou Art the Ruler of the Minds of All People'[4][2] | |
National song 'Vande Mataram'(Sanskrit) 'I Bow to Thee, Mother'[a][1][2] | |
Area controlled by India shown in dark green; regions claimed but not controlled shown in light green | |
| Capital | New Delhi 28°36′50″N77°12′30″E / 28.61389°N 77.20833°E |
| Largest city | |
| Official languages | |
| Recognised regional languages | |
| National language | None[9][10][11] |
| Religion |
|
| Demonym(s) | Indian |
| Membership | UN, WTO, BRICS, SAARC, SCO, G8+5, G20, Commonwealth of Nations |
| Government | |
| Ram Nath Kovind | |
• Vice President | Venkaiah Naidu |
| Narendra Modi | |
• Chief Justice | Ranjan Gogoi |
| Om Birla | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
• Upper house | Rajya Sabha |
| Lok Sabha | |
| Independence from the United Kingdom | |
| 15 August 1947 | |
• Republic | 26 January 1950 |
| Area | |
| 3,287,263[6] km2 (1,269,219 sq mi)[d] (7th) | |
• Water (%) | 9.6 |
| Population | |
| 1,324,171,354[13] (2nd) | |
• 2011 census | 1,210,854,977[14][15] (2nd) |
| 402.1/km2 (1,041.4/sq mi) (31st) | |
| GDP(PPP) | 2019 estimate |
• Total | $11.468 trillion[16] (3rd) |
| $8,484[16] (116th) | |
| GDP(nominal) | 2019 estimate |
• Total | $2.972 trillion[16] (7th) |
| $2,199[16] (133rd) | |
| Gini(2013) | 33.9[17] medium · 79th |
| HDI(2017) | 0.640[18] medium · 130th |
| Currency | Indian rupee (₹) (INR) |
| Time zone | UTC+05:30 (IST) |
| DST is not observed | |
| Date format | dd-mm-yyyy |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +91 |
| ISO 3166 code | IN |
| Internet TLD | .in (others) |
About Endonyms. An endonym is the name for a place, site or location in the language of the people who live there. These names may be officially designated by the local government or they may simply be widely used. This map depicts endonyms of the countries of the world in their official or national languages. Jammu and Kashmir, the northern most state of the India. You can find maps including its districts, cities, roads, railways, business and travel and tourism information. 8 º 12 º 16 º 20 º 23.5 º 24 º 28 º 32 º 36 º 68 º 72 º 76 º 80 º 84 º 88 º 92 º 96 º Shoreline Boundary of Indian Claim International Boundary (Undisputed) Line of Control (Disputed) Boundary of Foreign Claim State / Union Territory Boundary Water Body Foreign Territory Indian claimed Chinese Territory Indian claimed Pakistani Territory Undefined Territory.
India (ISO: Bhārat), also known as the Republic of India (ISO: Bhārat Gaṇarājya),[19][e] is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west;[f]China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand and Indonesia.
The Indian subcontinent was home to the Indus Valley Civilisation of the bronze age. In India's iron age, the oldest scriptures of Hinduism were composed, social stratification based on caste emerged, and Buddhism and Jainism arose. Political consolidations took place under the Maurya and Gupta Empires; the peninsular Middle Kingdoms influenced the cultures of Southeast Asia. In India's medieval era, Judaism, Zoroastrianism, Christianity, and Islam arrived, and Sikhism emerged, adding to a diverse culture. North India fell to the Delhi Sultanate; south India was united under the Vijayanagara Empire. In the early modern era, the expansive Mughal Empire was followed by East India Company rule. India's modern age was marked by British Crown rule and a nationalist movement which, under Mahatma Gandhi, was noted for nonviolence and led to India's independence in 1947.
Economic liberalisation, begun in 1991, has caused India to become a fast growing major economy and a newly industrialised country. Its gross domestic product ranks sixth in the world in market exchange rates and third in purchasing power parity.[16] Its per capita income ranks 133rd and 116th in the two measures.[16] India faces challenges of poverty, corruption, malnutrition, and inadequate public healthcare. A nuclear weapons state and regional power, it has the second largest active military in the world and ranks high in military expenditure. India is a secular, federal republic, governed in a democratic parliamentary system, and administered in 29 states and seven union territories. A pluralistic, multilingual and multi-ethnic society, India is home to 1.3 billion people. It is also home to a high diversity of wildlife in a variety of protected habitats.[20]
- 2History
- 5Politics and government
- 7Economy
- 8Demographics
- 9Culture
Etymology
The name India is derived from Indus, which originates from the Old Persian word Hindush, equivalent to the Sanskrit word Sindhu,[21] which was the historical local appellation for the Indus River.[22] The ancient Greeks referred to the Indians as Indoi (Ἰνδοί), which translates as 'The people of the Indus'.[23]
The geographical term Bharat (Bhārat; pronounced [ˈbʱaːɾət](listen)), which is recognised by the Constitution of India as an official name for the country,[19][24] is used by many Indian languages in its variations. It is a modernisation of the historical name Bharatavarsha, which traditionally referred to the Indian subcontinent and gained increasing currency from the mid-19th century as a native name for India.[19][25]
Hindustan ([ɦɪndʊˈstaːn](listen)) is a Middle Persian name for India. It was introduced into India by the Mughals and widely used since then. Its meaning varied, referring to a region that encompassed northern India and Pakistan or India in its entirety.[19][25][26] Currently, the name may refer to either the northern part of India or the entire country.[26]

History
Ancient India
The earliest known human remains in South Asia date to about 30,000 years ago.[27] Nearly contemporaneous human rock art sites have been found in many parts of the Indian subcontinent, including at the Bhimbetka rock shelters in Madhya Pradesh.[28] After 6500 BCE, evidence for domestication of food crops and animals, construction of permanent structures, and storage of agricultural surplus, appeared in Mehrgarh and other sites in what is now Balochistan.[29] These gradually developed into the Indus Valley Civilisation,[30][29] the first urban culture in South Asia,[31] which flourished during 2500–1900 BCE in what is now Pakistan and western India.[32] Centred around cities such as Mohenjo-daro, Harappa, Dholavira, and Kalibangan, and relying on varied forms of subsistence, the civilization engaged robustly in crafts production and wide-ranging trade.[31]
During the period 2000–500 BCE, many regions of the subcontinent transitioned from the Chalcolithic cultures to the Iron Age ones.[33] The Vedas, the oldest scriptures associated with Hinduism,[34] were composed during this period,[35] and historians have analysed these to posit a Vedic culture in the Punjab region and the upper Gangetic Plain.[33] Most historians also consider this period to have encompassed several waves of Indo-Aryan migration into the subcontinent from the north-west.[34] The caste system, which created a hierarchy of priests, warriors, and free peasants, but which excluded indigenous peoples by labeling their occupations impure, arose during this period.[36] On the Deccan Plateau, archaeological evidence from this period suggests the existence of a chiefdom stage of political organisation.[33] In South India, a progression to sedentary life is indicated by the large number of megalithic monuments dating from this period,[37] as well as by nearby traces of agriculture, irrigation tanks, and craft traditions.[37]
In the late Vedic period, around the 6th century BCE, the small states and chiefdoms of the Ganges Plain and the north-western regions had consolidated into 16 major oligarchies and monarchies that were known as the mahajanapadas.[38][39] The emerging urbanisation gave rise to non-Vedic religious movements, two of which became independent religions. Jainism came into prominence during the life of its exemplar, Mahavira.[40] Buddhism, based on the teachings of Gautama Buddha, attracted followers from all social classes excepting the middle class; chronicling the life of the Buddha was central to the beginnings of recorded history in India.[41][42][43] In an age of increasing urban wealth, both religions held up renunciation as an ideal,[44] and both established long-lasting monastic traditions. Politically, by the 3rd century BCE, the kingdom of Magadha had annexed or reduced other states to emerge as the Mauryan Empire.[45] The empire was once thought to have controlled most of the subcontinent excepting the far south, but its core regions are now thought to have been separated by large autonomous areas.[46][47] The Mauryan kings are known as much for their empire-building and determined management of public life as for Ashoka's renunciation of militarism and far-flung advocacy of the Buddhist dhamma.[48][49]
The Sangam literature of the Tamil language reveals that, between 200 BCE and 200 CE, the southern peninsula was being ruled by the Cheras, the Cholas, and the Pandyas, dynasties that traded extensively with the Roman Empire and with West and South-East Asia.[50][51] In North India, Hinduism asserted patriarchal control within the family, leading to increased subordination of women.[52][45] By the 4th and 5th centuries, the Gupta Empire had created in the greater Ganges Plain a complex system of administration and taxation that became a model for later Indian kingdoms.[53][54] Under the Guptas, a renewed Hinduism based on devotion rather than the management of ritual began to assert itself.[55] The renewal was reflected in a flowering of sculpture and architecture, which found patrons among an urban elite.[54]Classical Sanskrit literature flowered as well, and Indian science, astronomy, medicine, and mathematics made significant advances.[54]
Medieval India
The Indian early medieval age, 600 CE to 1200 CE, is defined by regional kingdoms and cultural diversity.[56] When Harsha of Kannauj, who ruled much of the Indo-Gangetic Plain from 606 to 647 CE, attempted to expand southwards, he was defeated by the Chalukya ruler of the Deccan.[57] When his successor attempted to expand eastwards, he was defeated by the Pala king of Bengal.[57] When the Chalukyas attempted to expand southwards, they were defeated by the Pallavas from farther south, who in turn were opposed by the Pandyas and the Cholas from still farther south.[57] No ruler of this period was able to create an empire and consistently control lands much beyond his core region.[56] During this time, pastoral peoples whose land had been cleared to make way for the growing agricultural economy were accommodated within caste society, as were new non-traditional ruling classes.[58] The caste system consequently began to show regional differences.[58]
In the 6th and 7th centuries, the first devotional hymns were created in the Tamil language.[59] They were imitated all over India and led to both the resurgence of Hinduism and the development of all modern languages of the subcontinent.[59] Indian royalty, big and small, and the temples they patronised drew citizens in great numbers to the capital cities, which became economic hubs as well.[60] Temple towns of various sizes began to appear everywhere as India underwent another urbanisation.[60] By the 8th and 9th centuries, the effects were felt in South-East Asia, as South Indian culture and political systems were exported to lands that became part of modern-day Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam, Philippines, Malaysia, and Java.[61] Indian merchants, scholars, and sometimes armies were involved in this transmission; South-East Asians took the initiative as well, with many sojourning in Indian seminaries and translating Buddhist and Hindu texts into their languages.[61]
After the 10th century, Muslim Central Asian nomadic clans, using swift-horse cavalry and raising vast armies united by ethnicity and religion, repeatedly overran South Asia's north-western plains, leading eventually to the establishment of the Islamic Delhi Sultanate in 1206.[62] The sultanate was to control much of North India and to make many forays into South India. Although at first disruptive for the Indian elites, the sultanate largely left its vast non-Muslim subject population to its own laws and customs.[63][64] By repeatedly repulsing Mongol raiders in the 13th century, the sultanate saved India from the devastation visited on West and Central Asia, setting the scene for centuries of migration of fleeing soldiers, learned men, mystics, traders, artists, and artisans from that region into the subcontinent, thereby creating a syncretic Indo-Islamic culture in the north.[65][66] The sultanate's raiding and weakening of the regional kingdoms of South India paved the way for the indigenous Vijayanagara Empire.[67] Embracing a strong Shaivite tradition and building upon the military technology of the sultanate, the empire came to control much of peninsular India,[68] and was to influence South Indian society for long afterwards.[67]
Early modern India
In the early 16th century, northern India, being then under mainly Muslim rulers,[69] fell again to the superior mobility and firepower of a new generation of Central Asian warriors.[70] The resulting Mughal Empire did not stamp out the local societies it came to rule, but rather balanced and pacified them through new administrative practices[71][72] and diverse and inclusive ruling elites,[73] leading to more systematic, centralised, and uniform rule.[74] Eschewing tribal bonds and Islamic identity, especially under Akbar, the Mughals united their far-flung realms through loyalty, expressed through a Persianised culture, to an emperor who had near-divine status.[73] The Mughal state's economic policies, deriving most revenues from agriculture[75] and mandating that taxes be paid in the well-regulated silver currency,[76] caused peasants and artisans to enter larger markets.[74] The relative peace maintained by the empire during much of the 17th century was a factor in India's economic expansion,[74] resulting in greater patronage of painting, literary forms, textiles, and architecture.[77] Newly coherent social groups in northern and western India, such as the Marathas, the Rajputs, and the Sikhs, gained military and governing ambitions during Mughal rule, which, through collaboration or adversity, gave them both recognition and military experience.[78] Expanding commerce during Mughal rule gave rise to new Indian commercial and political elites along the coasts of southern and eastern India.[78] As the empire disintegrated, many among these elites were able to seek and control their own affairs.[79]
By the early 18th century, with the lines between commercial and political dominance being increasingly blurred, a number of European trading companies, including the English East India Company, had established coastal outposts.[80][81] The East India Company's control of the seas, greater resources, and more advanced military training and technology led it to increasingly flex its military muscle and caused it to become attractive to a portion of the Indian elite; these factors were crucial in allowing the company to gain control over the Bengal region by 1765 and sideline the other European companies.[82][80][83][84] Its further access to the riches of Bengal and the subsequent increased strength and size of its army enabled it to annex or subdue most of India by the 1820s.[85] India was then no longer exporting manufactured goods as it long had, but was instead supplying the British Empire with raw materials, and many historians consider this to be the onset of India's colonial period.[80] By this time, with its economic power severely curtailed by the British parliament and effectively having been made an arm of British administration, the company began to more consciously enter non-economic arenas such as education, social reform, and culture.[86]
Modern India
Historians consider India's modern age to have begun sometime between 1848 and 1885. The appointment in 1848 of Lord Dalhousie as Governor General of the East India Company set the stage for changes essential to a modern state. These included the consolidation and demarcation of sovereignty, the surveillance of the population, and the education of citizens. Technological changes—among them, railways, canals, and the telegraph—were introduced not long after their introduction in Europe.[87][88][89][90] However, disaffection with the company also grew during this time, and set off the Indian Rebellion of 1857. Fed by diverse resentments and perceptions, including invasive British-style social reforms, harsh land taxes, and summary treatment of some rich landowners and princes, the rebellion rocked many regions of northern and central India and shook the foundations of Company rule.[91][92] Although the rebellion was suppressed by 1858, it led to the dissolution of the East India Company and the direct administration of India by the British government. Proclaiming a unitary state and a gradual but limited British-style parliamentary system, the new rulers also protected princes and landed gentry as a feudal safeguard against future unrest.[93][94] In the decades following, public life gradually emerged all over India, leading eventually to the founding of the Indian National Congress in 1885.[95][96][97][98]
The rush of technology and the commercialisation of agriculture in the second half of the 19th century was marked by economic setbacks—many small farmers became dependent on the whims of far-away markets.[99] There was an increase in the number of large-scale famines,[100] and, despite the risks of infrastructure development borne by Indian taxpayers, little industrial employment was generated for Indians.[101] There were also salutary effects: commercial cropping, especially in the newly canalled Punjab, led to increased food production for internal consumption.[102] The railway network provided critical famine relief,[103] notably reduced the cost of moving goods,[103] and helped the nascent Indian-owned industry.[102]
After World War I, in which approximately one million Indians served,[104] a new period began. It was marked by British reforms but also repressive legislation, by more strident Indian calls for self-rule, and by the beginnings of a nonviolent movement of non-co-operation, of which Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi would become the leader and enduring symbol.[105] During the 1930s, slow legislative reform was enacted by the British; the Indian National Congress won victories in the resulting elections.[106] The next decade was beset with crises: Indian participation in World War II, the Congress's final push for non-co-operation, and an upsurge of Muslim nationalism. All were capped by the advent of independence in 1947, but tempered by the partition of India into two states: India and Pakistan.[107]
Vital to India's self-image as an independent nation was its constitution, completed in 1950, which put in place a secular and democratic republic.[108] It has remained a democracy with civil liberties, an active Supreme Court, and a largely independent press.[109] Economic liberalisation, which was begun in the 1990s, has created a large urban middle class, transformed India into one of the world's fastest-growing economies,[110] and increased its geopolitical clout. Indian movies, music, and spiritual teachings play an increasing role in global culture.[109] Yet, India is also shaped by seemingly unyielding poverty, both rural and urban;[109] by religious and caste-related violence;[111] by Maoist-inspired Naxalite insurgencies;[112] and by separatism in Jammu and Kashmir and in Northeast India.[113] It has unresolved territorial disputes with China[114] and with Pakistan.[114] The India–Pakistan nuclear rivalry came to a head in 1998.[115] India's sustained democratic freedoms are unique among the world's newer nations; however, in spite of its recent economic successes, freedom from want for its disadvantaged population remains a goal yet to be achieved.[116]
Geography
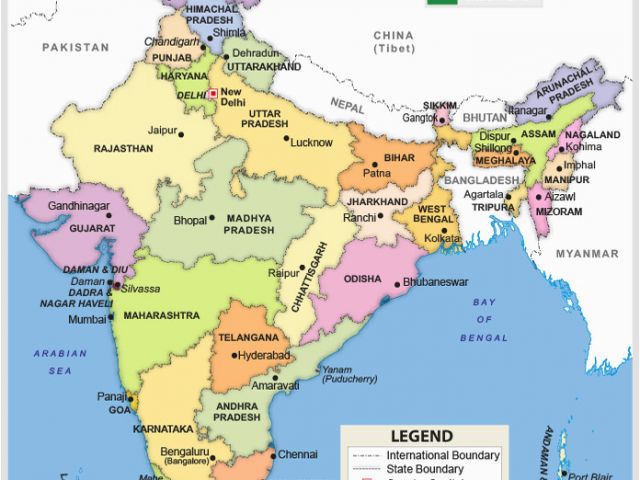
Map Of India With States
India comprises the bulk of the Indian subcontinent, lying atop the Indian tectonic plate, a part of the Indo-Australian Plate.[117] India's defining geological processes began 75 million years ago when the Indian plate, then part of the southern supercontinent Gondwana, began a north-eastward drift caused by seafloor spreading to its south-west and, later, south and south-east.[117] Simultaneously, the vast Tethynoceanic crust, to its northeast, began to subduct under the Eurasian plate.[117] These dual processes, driven by convection in the Earth's mantle, both created the Indian Ocean and caused the Indian continental crust eventually to under-thrust Eurasia and to uplift the Himalayas.[117] Immediately south of the emerging Himalayas, plate movement created a vast trough that rapidly filled with river-borne sediment[118] and now constitutes the Indo-Gangetic Plain.[119] Cut off from the plain by the ancient Aravalli Range lies the Thar Desert.[120]
The original Indian plate survives as peninsular India, the oldest and geologically most stable part of India. It extends as far north as the Satpura and Vindhya ranges in central India. These parallel chains run from the Arabian Sea coast in Gujarat in the west to the coal-rich Chota Nagpur Plateau in Jharkhand in the east.[121] To the south, the remaining peninsular landmass, the Deccan Plateau, is flanked on the west and east by coastal ranges known as the Western and Eastern Ghats;[122] the plateau contains the country's oldest rock formations, some over one billion years old. Constituted in such fashion, India lies to the north of the equator between 6° 44' and 35° 30' north latitude[g] and 68° 7' and 97° 25' east longitude.[123]
India's coastline measures 7,517 kilometres (4,700 mi) in length; of this distance, 5,423 kilometres (3,400 mi) belong to peninsular India and 2,094 kilometres (1,300 mi) to the Andaman, Nicobar, and Lakshadweep island chains.[124] According to the Indian naval hydrographic charts, the mainland coastline consists of the following: 43% sandy beaches; 11% rocky shores, including cliffs; and 46% mudflats or marshy shores.[124]
Major Himalayan-origin rivers that substantially flow through India include the Ganges and the Brahmaputra, both of which drain into the Bay of Bengal.[125] Important tributaries of the Ganges include the Yamuna and the Kosi; the latter's extremely low gradient often leads to severe floods and course changes.[126] Major peninsular rivers, whose steeper gradients prevent their waters from flooding, include the Godavari, the Mahanadi, the Kaveri, and the Krishna, which also drain into the Bay of Bengal;[127] and the Narmada and the Tapti, which drain into the Arabian Sea.[128] Coastal features include the marshy Rann of Kutch of western India and the alluvial Sundarbans delta of eastern India; the latter is shared with Bangladesh.[129] India has two archipelagos: the Lakshadweep, coral atolls off India's south-western coast; and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a volcanic chain in the Andaman Sea.[130]
The Indian climate is strongly influenced by the Himalayas and the Thar Desert, both of which drive the economically and culturally pivotal summer and winter monsoons.[131] The Himalayas prevent cold Central Asian katabatic winds from blowing in, keeping the bulk of the Indian subcontinent warmer than most locations at similar latitudes.[132][133] The Thar Desert plays a crucial role in attracting the moisture-laden south-west summer monsoon winds that, between June and October, provide the majority of India's rainfall.[131] Four major climatic groupings predominate in India: tropical wet, tropical dry, subtropical humid, and montane.[134]
Biodiversity
India lies within the Indomalaya ecozone and contains three biodiversity hotspots.[135] One of 17 megadiverse countries, it hosts 8.6% of all mammalian, 13.7% of all avian, 7.9% of all reptilian, 6% of all amphibian, 12.2% of all piscine, and 6.0% of all flowering plant species.[136][137] About 21.2% of the country's landmass is covered by forests (tree canopy density >10%), of which 12.2% comprises moderately or very dense forests (tree canopy density >40%).[138]Endemism is high among plants, 33%, and among ecoregions such as the sholaforests.[139] Habitat ranges from the tropical rainforest of the Andaman Islands, Western Ghats, and North-East India to the coniferous forest of the Himalaya. Between these extremes lie the moist deciduous sal forest of eastern India; the dry deciduous teak forest of central and southern India; and the babul-dominated thorn forest of the central Deccan and western Gangetic plain.[140] The medicinal neem, widely used in rural Indian herbal remedies, is a key Indian tree.[141] The luxuriant pipal fig tree,[142] shown on the seals of Mohenjo-daro,[143] shaded Gautama Buddha as he sought enlightenment.[144]
Many Indian species descend from taxa originating in Gondwana, from which the Indian plate separated more than 105 million years Before Present.[145]Peninsular India's subsequent movement towards and collision with the Laurasian landmass set off a mass exchange of species. Epochal volcanism and climatic changes 20 million years ago forced a mass extinction.[146] Mammals then entered India from Asia through two zoogeographical passes flanking the rising Himalaya.[140] Thus, while 45.8% of reptiles and 55.8% of amphibians are endemic, only 12.6% of mammals and 4.5% of birds are.[137] Among them are the Nilgiri leaf monkey and Beddome's toad of the Western Ghats. India contains 172 IUCN-designated threatened animal species, or 2.9% of endangered forms.[147]
The pervasive and ecologically devastating human encroachment of recent decades has critically endangered Indian wildlife. In response, the system of national parks and protected areas, first established in 1935, was substantially expanded. In 1972, India enacted the Wildlife Protection Act[148] and Project Tiger to safeguard crucial wilderness; the Forest Conservation Act was enacted in 1980 and amendments added in 1988.[149] India hosts more than five hundred wildlife sanctuaries and thirteenbiosphere reserves,[150] four of which are part of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves; twenty-five wetlands are registered under the Ramsar Convention.[151]
Politics and government
Politics
India is the world's most populous democracy.[152] A parliamentary republic with a multi-party system,[153] it has sevenrecognised national parties, including the Indian National Congress and the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), and more than 40regional parties.[154] The Congress is considered centre-left in Indian political culture,[155] and the BJP right-wing.[156][157][158] For most of the period between 1950—when India first became a republic—and the late 1980s, the Congress held a majority in the parliament. Since then, however, it has increasingly shared the political stage with the BJP,[159] as well as with powerful regional parties which have often forced the creation of multi-party coalition governments at the centre.[160]
In the Republic of India's first three general elections, in 1951, 1957, and 1962, the Jawaharlal Nehru-led Congress won easy victories. On Nehru's death in 1964, Lal Bahadur Shastri briefly became prime minister; he was succeeded, after his own unexpected death in 1966, by Indira Gandhi, who went on to lead the Congress to election victories in 1967 and 1971. Following public discontent with the state of emergency she declared in 1975, the Congress was voted out of power in 1977; the then-new Janata Party, which had opposed the emergency, was voted in. Its government lasted just over two years. Voted back into power in 1980, the Congress saw a change in leadership in 1984, when Indira Gandhi was assassinated; she was succeeded by her son Rajiv Gandhi, who won an easy victory in the general elections later that year. The Congress was voted out again in 1989 when a National Front coalition, led by the newly formed Janata Dal in alliance with the Left Front, won the elections; that government too proved relatively short-lived, lasting just under two years.[161] Elections were held again in 1991; no party won an absolute majority. The Congress, as the largest single party, was able to form a minority government led by P. V. Narasimha Rao.[162]
A two-year period of political turmoil followed the general election of 1996. Several short-lived alliances shared power at the centre. The BJP formed a government briefly in 1996; it was followed by two comparatively long-lasting United Front coalitions, which depended on external support. In 1998, the BJP was able to form a successful coalition, the National Democratic Alliance (NDA). Led by Atal Bihari Vajpayee, the NDA became the first non-Congress, coalition government to complete a five-year term.[163] In the 2004 Indian general elections, again no party won an absolute majority, but the Congress emerged as the largest single party, forming another successful coalition: the United Progressive Alliance (UPA). It had the support of left-leaning parties and MPs who opposed the BJP. The UPA returned to power in the 2009 general election with increased numbers, and it no longer required external support from India's communist parties.[164] That year, Manmohan Singh became the first prime minister since Jawaharlal Nehru in 1957 and 1962 to be re-elected to a consecutive five-year term.[165] In the 2014 general election, the BJP became the first political party since 1984 to win a majority and govern without the support of other parties.[166] The incumbent Indian prime minister is Narendra Modi, a former chief minister of Gujarat. On 20 July 2017, Ram Nath Kovind was elected India's 14th president and took the oath of office on 25 July 2017.[167][168][169]
Government
India is a federation with a parliamentary system governed under the Constitution of India, which serves as the country's supreme legal document. It is a constitutional republic and representative democracy, in which 'majority rule is tempered by minority rights protected by law'. Federalism in India defines the power distribution between the union, or central, government and the states. The government abides by constitutional checks and balances. The Constitution of India, which came into effect on 26 January 1950,[170] states in its preamble that India is a sovereign, socialist, secular, democraticrepublic.[171] India's form of government, traditionally described as 'quasi-federal' with a strong centre and weak states,[172] has grown increasingly federal since the late 1990s as a result of political, economic, and social changes.[173][174]
| Flag | Tiranga (Tricolour) |
|---|---|
| Emblem | Sarnath Lion Capital |
| Language | None[9][10][11] |
| Anthem | Jana Gana Mana |
| Song | Vande Mataram |
| Currency | ₹ (Indian rupee) |
| Calendar | Saka |
| Animal | Tiger (land) River dolphin (aquatic) |
| Bird | Indian peafowl |
| Flower | Lotus |
| Fruit | Mango |
| Tree | Banyan |
| River | Ganga |
| Game | Not declared[175] |
The Government of India comprises three branches:[176]
- Executive: The President of India is the ceremonial head of state,[177] who is elected indirectly for a five-year term by an electoral college comprising members of national and state legislatures.[178][179] The Prime Minister of India is the head of government and exercises most executive power.[180] Appointed by the president,[181] the prime minister is by convention supported by the party or political alliance having a majority of seats in the lower house of parliament.[180] The executive of the Indian government consists of the president, the vice president, and the Union Council of Ministers—with the cabinet being its executive committee—headed by the prime minister. Any minister holding a portfolio must be a member of one of the houses of parliament.[177] In the Indian parliamentary system, the executive is subordinate to the legislature; the prime minister and his or her council are directly responsible to the lower house of the parliament. The civil servants act as permanent executives and all decisions of the executive are implemented by them. [182]
- Legislature: The legislature of India is the bicameralparliament. Operating under a Westminster-style parliamentary system, it comprises an upper house called the Rajya Sabha (Council of States) and a lower house called the Lok Sabha (House of the People).[183] The Rajya Sabha is a permanent body of 245members who serve staggered six-yearterms.[184] Most are elected indirectly by the state and union territorial legislatures in numbers proportional to their state's share of the national population.[181] All but two of the Lok Sabha's 545members are directly elected by popular vote; they represent single-member constituencies for five-yearterms.[185] The remaining twomembers are nominated by the president from among the Anglo-Indian community, in case the president decides that they are not adequately represented.[186]
- Judiciary: India has a three-tierunitary independent judiciary[187] comprising the supreme court, headed by the Chief Justice of India, 24high courts, and a large number of trial courts.[187] The supreme court has original jurisdiction over cases involving fundamental rights and over disputes between states and the centre and has appellate jurisdiction over the high courts.[188] It has the power to both strike down union or state laws which contravene the constitution,[189] and invalidate any government action it deems unconstitutional.[190]
Administrative divisions
| 1. Andhra Pradesh | 19. Nagaland |
| 2. Arunachal Pradesh | 20. Odisha |
| 3. Assam | 21. Punjab |
| 4. Bihar | 22. Rajasthan |
| 5. Chhattisgarh | 23. Sikkim |
| 6. Goa | 24. Tamil Nadu |
| 7. Gujarat | 25. Telangana |
| 8. Haryana | 26. Tripura |
| 9. Himachal Pradesh | 27. Uttar Pradesh |
| 10. Jammu and Kashmir | 28. Uttarakhand |
| 11. Jharkhand | 29. West Bengal |
| 12. Karnataka | A. Andaman and Nicobar Islands |
| 13. Kerala | B. Chandigarh |
| 14. Madhya Pradesh | C. Dadra and Nagar Haveli |
| 15. Maharashtra | D. Daman and Diu |
| 16. Manipur | E. Lakshadweep |
| 17. Meghalaya | F. National Capital Territory of Delhi |
| 18. Mizoram | G. Puducherry |
India is a federal union comprising 29 states and 7 union territories.[191] All states, as well in addition to the union territories of Puducherry and the National Capital Territory of Delhi, have elected legislatures and governments following on the Westminster system of governance. The remaining five union territories are directly ruled by the centre through appointed administrators. In 1956, under the States Reorganisation Act, states were reorganised on a linguistic basis.[192] Since then, their structure has remained largely unchanged. Each state or union territory is further divided into administrative districts. The districts are further divided into tehsils and ultimately into villages.
Foreign, economic and strategic relations

Since its independence in 1947, India has maintained cordial relations with most nations. In the 1950s, it strongly supported decolonisation in Africa and Asia and played a lead role in the Non-Aligned Movement.[193] In the late 1980s, the Indian military twice intervened abroad at the invitation of neighbouring countries: a peace-keeping operation in Sri Lanka between 1987 and 1990; and an armed intervention to prevent a 1988 coup d'état attempt in the Maldives. India has tense relations with neighbouring Pakistan; the two nations have gone to war four times: in 1947, 1965, 1971, and 1999. Three of these wars were fought over the disputed territory of Kashmir, while the fourth, the 1971 war, followed from India's support for the independence of Bangladesh.[194] After waging the 1962 Sino-Indian War and the 1965 war with Pakistan, India pursued close military and economic ties with the Soviet Union; by the late 1960s, the Soviet Union was its largest arms supplier.[195]
Aside from ongoing special relationship with Russia,[196] India has wide-ranging defence relations with Israel and France. In recent years, it has played key roles in the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation and the World Trade Organization. The nation has provided 100,000 military and police personnel to serve in 35 UN peacekeeping operations across four continents. It participates in the East Asia Summit, the G8+5, and other multilateral forums.[197] India has close economic ties with South America,[198] Asia, and Africa; it pursues a 'Look East' policy that seeks to strengthen partnerships with the ASEAN nations, Japan, and South Korea that revolve around many issues, but especially those involving economic investment and regional security.[199][200]
China's nuclear test of 1964, as well as its repeated threats to intervene in support of Pakistan in the 1965 war, convinced India to develop nuclear weapons.[201] India conducted its first nuclear weapons test in 1974 and carried out further underground testing in 1998. Despite criticism and military sanctions, India has signed neither the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty nor the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty, considering both to be flawed and discriminatory.[202] India maintains a 'no first use' nuclear policy and is developing a nuclear triad capability as a part of its 'Minimum Credible Deterrence' doctrine.[203][204] It is developing a ballistic missile defence shield and, in collaboration with Russia, a fifth-generation fighter jet.[205] Other indigenous military projects involve the design and implementation of Vikrant-class aircraft carriers and Arihant-class nuclear submarines.[205]
Since the end of the Cold War, India has increased its economic, strategic, and military co-operation with the United States and the European Union.[206] In 2008, a civilian nuclear agreement was signed between India and the United States. Although India possessed nuclear weapons at the time and was not party to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty, it received waivers from the International Atomic Energy Agency and the Nuclear Suppliers Group, ending earlier restrictions on India's nuclear technology and commerce. As a consequence, India became the sixth de facto nuclear weapons state.[207] India subsequently signed co-operation agreements involving civilian nuclear energy with Russia,[208] France,[209] the United Kingdom,[210] and Canada.[211]
The President of India is the supreme commander of the nation's armed forces; with 1.395 million active troops, they compose the world's second-largest military. It comprises the Indian Army, the Indian Navy, the Indian Air Force, and the Indian Coast Guard.[212] The official Indian defence budget for 2011 was US$36.03 billion, or 1.83% of GDP.[213] For the fiscal year spanning 2012–2013, US$40.44 billion was budgeted.[214] According to a 2008 SIPRI report, India's annual military expenditure in terms of purchasing power stood at US$72.7 billion.[215] In 2011, the annual defence budget increased by 11.6%,[216] although this does not include funds that reach the military through other branches of government.[217] As of 2012, India is the world's largest arms importer; between 2007 and 2011, it accounted for 10% of funds spent on international arms purchases.[218] Much of the military expenditure was focused on defence against Pakistan and countering growing Chinese influence in the Indian Ocean.[216] In May 2017, the Indian Space Research Organisation launched the South Asia Satellite, a gift from India to its neighbouring SAARC countries.[219] In October 2018, India signed a US$5.43 billion (over Rs 400 billion) agreement with Russia to procure four S-400 Triumf surface-to-air missile defence systems, Russia's most advanced long-range missile defence system.[220]
Economy
According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), the Indian economy in 2017 was nominally worth US$2.611 trillion; it is the sixth-largest economy by market exchange rates, and is, at US$9.459 trillion, the third-largest by purchasing power parity, or PPP.[16] With its average annual GDP growth rate of 5.8% over the past two decades, and reaching 6.1% during 2011–12,[221] India is one of the world's fastest-growing economies.[222] However, the country ranks 140th in the world in nominal GDP per capita and 129th in GDP per capita at PPP.[223] Until 1991, all Indian governments followed protectionist policies that were influenced by socialist economics. Widespread state intervention and regulation largely walled the economy off from the outside world. An acute balance of payments crisis in 1991 forced the nation to liberalise its economy;[224] since then it has slowly moved towards a free-market system[225][226] by emphasising both foreign trade and direct investment inflows.[227] India has been a member of WTO since 1 January 1995.[228]
The 513.7-million-worker Indian labour force is the world's second-largest, as of 2016.[212] The service sector makes up 55.6% of GDP, the industrial sector 26.3% and the agricultural sector 18.1%. India's foreign exchange remittances of US$70 billion in 2014, the largest in the world, contributed to its economy by 25 million Indians working in foreign countries.[229] Major agricultural products include rice, wheat, oilseed, cotton, jute, tea, sugarcane, and potatoes.[191] Major industries include textiles, telecommunications, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, food processing, steel, transport equipment, cement, mining, petroleum, machinery, and software.[191] In 2006, the share of external trade in India's GDP stood at 24%, up from 6% in 1985.[225] In 2008, India's share of world trade was 1.68%;[230] In 2011, India was the world's tenth-largest importer and the nineteenth-largest exporter.[231] Major exports include petroleum products, textile goods, jewellery, software, engineering goods, chemicals, and leather manufactures.[191] Major imports include crude oil, machinery, gems, fertiliser, and chemicals.[191] Between 2001 and 2011, the contribution of petrochemical and engineering goods to total exports grew from 14% to 42%.[232] India was the second largest textile exporter after China in the world in the calendar year 2013.[233]
Averaging an economic growth rate of 7.5% for several years prior to 2007,[225] India has more than doubled its hourly wage rates during the first decade of the 21st century.[234] Some 431 million Indians have left poverty since 1985; India's middle classes are projected to number around 580 million by 2030.[235] Though ranking 51st in global competitiveness, India ranks 17th in financial market sophistication, 24th in the banking sector, 44th in business sophistication, and 39th in innovation, ahead of several advanced economies, as of 2010.[236] With 7 of the world's top 15 information technology outsourcing companies based in India, the country is viewed as the second-most favourable outsourcing destination after the United States, as of 2009.[237] India's consumer market, the world's eleventh-largest, is expected to become fifth-largest by 2030.[235] However, hardly 2% of Indians pay income taxes.[238]
Driven by growth, India's nominal GDP per capita has steadily increased from US$329 in 1991, when economic liberalisation began, to US$1,265 in 2010, to an estimated US$1,723 in 2016, and is expected to grow to US$2,358 by 2020;[16] however, it has remained lower than those of other Asian developing countries such as Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Sri Lanka, and Thailand, and is expected to remain so in the near future. However, it is higher than Pakistan, Nepal, Afghanistan, Bangladesh and others.[239]
According to a 2011 PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC) report, India's GDP at purchasing power parity could overtake that of the United States by 2045.[240] During the next four decades, Indian GDP is expected to grow at an annualised average of 8%, making it potentially the world's fastest-growing major economy until 2050.[240] The report highlights key growth factors: a young and rapidly growing working-age population; growth in the manufacturing sector because of rising education and engineering skill levels; and sustained growth of the consumer market driven by a rapidly growing middle-class.[240] The World Bank cautions that, for India to achieve its economic potential, it must continue to focus on public sector reform, transport infrastructure, agricultural and rural development, removal of labour regulations, education, energy security, and public health and nutrition.[241]
According to the Worldwide Cost of Living Report 2017 released by the Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU) which was created by comparing more than 400 individual prices across 160 products and services, four of the cheapest cities were in India: Bangalore (3rd), Mumbai (5th), Chennai (5th) and New Delhi (8th).[242]
Industries
India's telecommunication industry, the world's fastest-growing, added 227 million subscribers during the period 2010–11,[243] and after the third quarter of 2017, India surpassed the US to become the second largest smartphone market in the world after China.[244]
The Indian automotive industry, the world's second-fastest growing, increased domestic sales by 26% during 2009–10,[245] and exports by 36% during 2008–09.[246] India's capacity to generate electrical power is 300 gigawatts, of which 42 gigawatts is renewable.[247] At the end of 2011, the Indian IT industry employed 2.8 million professionals, generated revenues close to US$100 billion equalling 7.5% of Indian GDP and contributed 26% of India's merchandise exports.[248]
The pharmaceutical industry in India is among the significant emerging markets for the global pharmaceutical industry. The Indian pharmaceutical market is expected to reach $48.5 billion by 2020. India's R & D spending constitutes 60% of the biopharmaceutical industry.[249][250] India is among the top 12 biotech destinations in the world.[251][252] The Indian biotech industry grew by 15.1% in 2012–13, increasing its revenues from 204.4 billion INR (Indian rupees) to 235.24 billion INR (3.94 B US$ – exchange rate June 2013: 1 US$ approx. 60 INR).[253]
Socio-economic challenges
Despite economic growth during recent decades, India continues to face socio-economic challenges. In 2006, India contained the largest number of people living below the World Bank's international poverty line of US$1.25 per day,[254] the proportion having decreased from 60% in 1981 to 42% in 2005;[255] under its later revised poverty line, it was 21% in 2011.[h][257] 30.7% of India's children under the age of five are underweight.[258] According to a Food and Agriculture Organization report in 2015, 15% of the population is undernourished.[259][260] The Mid-Day Meal Scheme attempts to lower these rates.[261]
According to a Walk Free Foundation report in 2016, there were an estimated 18.3 million people in India, or 1.4% of the population, living in the forms of modern slavery, such as bonded labour, child labour, human trafficking, and forced begging, among others.[262][263][264] According to the 2011 census, there were 10.1 million child labourers in the country, a decline of 2.6 million from 12.6 million child labourers in 2001.[265]
Since 1991, economic inequality between India's states has consistently grown: the per-capita net state domestic product of the richest states in 2007 was 3.2 times that of the poorest.[266]Corruption in India is perceived to have decreased. According to Corruption Perceptions Index, India ranked 76th out of 176 countries in 2016, from 85th in 2014.[267]
Demographics
| Population[13] | |
|---|---|
| Year | Million |
| 1970 | 553.6 |
| 2000 | 1053.0 |
| 2016 | 1324.2 |
With 1,210,193,422 residents reported in the 2011 provisional census report,[268] India is the world's second-most populous country. Its population grew by 17.64% during 2001–2011,[269] compared to 21.54% growth in the previous decade (1991–2001).[269] The human sex ratio, according to the 2011 census, is 940 females per 1,000 males.[268] The median age was 27.6 as of 2016.[212] The first post-colonial census, conducted in 1951, counted 361.1 million people.[270] Medical advances made in the last 50 years as well as increased agricultural productivity brought about by the 'Green Revolution' have caused India's population to grow rapidly.[271] India continues to face several public health-related challenges.[272][273]
Life expectancy in India is at 68 years, with life expectancy for women being 69.6 years and for men being 67.3.[274] There are around 50 physicians per 100,000 Indians.[275] Migration from rural to urban areas has been an important dynamic in the recent history of India. The number of Indians living in urban areas grew by 31.2% between 1991 and 2001.[276] Yet, in 2001, over 70% still lived in rural areas.[277][278] The level of urbanisation increased further from 27.81% in the 2001 Census to 31.16% in the 2011 Census. The slowing down of the overall growth rate of population was due to the sharp decline in the growth rate in rural areas since 1991.[279] According to the 2011 census, there are 53 million-plus urban agglomerations in India; among them Mumbai, Delhi, Kolkata, Chennai, Bangalore, Hyderabad and Ahmedabad, in decreasing order by population.[280] The literacy rate in 2011 was 74.04%: 65.46% among females and 82.14% among males.[281] The rural-urban literacy gap, which was 21.2 percentage points in 2001, dropped to 16.1 percentage points in 2011. The improvement in literacy rate in rural area is two times that in urban areas.[279]Kerala is the most literate state with 93.91% literacy; while Bihar the least with 63.82%.[281]
Languages
India is home to two major language families: Indo-Aryan (spoken by about 74% of the population) and Dravidian (spoken by 24% of the population). Other languages spoken in India come from the Austroasiatic and Sino-Tibetan language families. India has no national language.[282]Hindi, with the largest number of speakers, is the official language of the government.[283][284]English is used extensively in business and administration and has the status of a 'subsidiary official language';[5] it is important in education, especially as a medium of higher education. Each state and union territory has one or more official languages, and the constitution recognises in particular 22 'scheduled languages'.
Religions
The 2011 census reported that the religion in India with the largest number of followers was Hinduism (79.80% of the population), followed by Islam (14.23%); the remaining were Christianity (2.30%), Sikhism (1.72%), Buddhism (0.70%), Jainism (0.36%) and others[c] (0.9%).[12] India has the world's largest Hindu, Sikh, Jain, Zoroastrian, and Bahá'í populations, and has the third-largest Muslim population—the largest for a non-Muslim majority country.[285][286]
Culture
Indian cultural history spans more than 4,500years.[287] During the Vedic period (c. 1700 – c. 500BCE), the foundations of Hindu philosophy, mythology, theology and literature were laid, and many beliefs and practices which still exist today, such as dhárma, kárma, yóga, and mokṣa, were established.[23] India is notable for its religious diversity, with Hinduism, Buddhism, Sikhism, Islam, Christianity, and Jainism among the nation's major religions.[288] The predominant religion, Hinduism, has been shaped by various historical schools of thought, including those of the Upanishads,[289] the Yoga Sutras, the Bhakti movement,[288] and by Buddhist philosophy.[290]
Art and architecture
Much of Indian architecture, including the Taj Mahal, other works of Mughal architecture, and South Indian architecture, blends ancient local traditions with imported styles.[291]Vernacular architecture is also highly regional in it flavours. Vastu shastra, literally 'science of construction' or 'architecture' and ascribed to Mamuni Mayan,[292] explores how the laws of nature affect human dwellings;[293] it employs precise geometry and directional alignments to reflect perceived cosmic constructs.[294] As applied in Hindu temple architecture, it is influenced by the Shilpa Shastras, a series of foundational texts whose basic mythological form is the Vastu-Purusha mandala, a square that embodied the 'absolute'.[295] The Taj Mahal, built in Agra between 1631 and 1648 by orders of Emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his wife, has been described in the UNESCO World Heritage List as 'the jewel of Muslim art in India and one of the universally admired masterpieces of the world's heritage'.[296]Indo-Saracenic Revival architecture, developed by the British in the late 19th century, drew on Indo-Islamic architecture.[297]
Literature
The earliest literature in India, composed between 1500 BCE and 1200 CE, was in the Sanskrit language.[298] Major works of Sanskrit literature include the Rigveda (c. 1500 BCE–1200 BCE), the epics:Mahābhārata (c. 400 BCE–400 CE) and the Ramayana (c. 300 BCE and later); Abhijñānaśākuntalam (The Recognition of Śakuntalā, and other dramas of Kālidāsa (c. 5th century CE) and Mahākāvya poetry.[299][300][301] In Tamil literature, Sangam Literature (c 600 BCE–300 BCE) consisting of 2,381 poems, composed by 473 poets, is the earliest work.[302][303][304][305] From the 14th to the 18th centuries, India's literary traditions went through a period of drastic change because of the emergence of devotional poets such as Kabīr, Tulsīdās, and Guru Nānak. This period was characterised by a varied and wide spectrum of thought and expression; as a consequence, medieval Indian literary works differed significantly from classical traditions.[306] In the 19th century, Indian writers took a new interest in social questions and psychological descriptions. In the 20th century, Indian literature was influenced by the works of Bengali poet and novelist Rabindranath Tagore,[307] who was a recipient of the Nobel Prize in Literature.
Performing arts
Indian music ranges over various traditions and regional styles. Classical music encompasses two genres and their various folk offshoots: the northern Hindustani and southern Carnatic schools.[308] Regionalised popular forms include filmi and folk music; the syncretic tradition of the bauls is a well-known form of the latter. Indian dance also features diverse folk and classical forms. Among the better-known folk dances are the bhangra of Punjab, the bihu of Assam, the Jhumair and chhau of Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal, garba and dandiya of Gujarat, ghoomar of Rajasthan, and the lavani of Maharashtra. Eight dance forms, many with narrative forms and mythological elements, have been accorded classical dance status by India's National Academy of Music, Dance, and Drama. These are: bharatanatyam of the state of Tamil Nadu, kathak of Uttar Pradesh, kathakali and mohiniyattam of Kerala, kuchipudi of Andhra Pradesh, manipuri of Manipur, odissi of Odisha, and the sattriya of Assam.[309]Theatre in India melds music, dance, and improvised or written dialogue.[310] Often based on Hindu mythology, but also borrowing from medieval romances or social and political events, Indian theatre includes the bhavai of Gujarat, the jatra of West Bengal, the nautanki and ramlila of North India, tamasha of Maharashtra, burrakatha of Andhra Pradesh, terukkuttu of Tamil Nadu, and the yakshagana of Karnataka.[311] India has a theatre training institute NSD that is situated at New Delhi It is an autonomous organisation under the Ministry of Culture, Government of India.[312]
Motion pictures, television
The Indian film industry produces the world's most-watched cinema.[313] Established regional cinematic traditions exist in the Assamese, Bengali, Bhojpuri, Hindi, Kannada, Malayalam, Punjabi, Gujarati, Marathi, Odia, Tamil, and Telugu languages.[314] South Indian cinema attracts more than 75% of national film revenue.[315]
Television broadcasting began in India in 1959 as a state-run medium of communication and had slow expansion for more than two decades.[316][317] The state monopoly on television broadcast ended in the 1990s and, since then, satellite channels have increasingly shaped the popular culture of Indian society.[318] Today, television is the most penetrative media in India; industry estimates indicate that as of 2012 there are over 554 million TV consumers, 462 million with satellite and/or cable connections, compared to other forms of mass media such as press (350 million), radio (156 million) or internet (37 million).[319]
Cuisine
Indian cuisine encompasses a wide variety of regional and traditional cuisines, often depending on a particular state (such as Maharashtrian cuisine). Staple foods of Indian cuisine include pearl millet (ISO: bājra), rice, whole-wheat flour (aṭṭa), and a variety of lentils, such as masoor (most often red lentils), toor (pigeon peas), urad (black gram), and mong (mung beans). Lentils may be used whole, dehusked—for example, dhuli moong or dhuli urad—or split. Split lentils, or dal, are used extensively.[320] The spice trade between India and Europe is often cited by historians as the primary catalyst for Europe's Age of Discovery.[321]
Society
Traditional Indian society is sometimes defined by social hierarchy. The Indian caste system embodies much of the social stratification and many of the social restrictions found in the Indian subcontinent. Social classes are defined by thousands of endogamous hereditary groups, often termed as jātis, or 'castes'.[322] India declared untouchability to be illegal[323] in 1947 and has since enacted other anti-discriminatory laws and social welfare initiatives. At the workplace in urban India and in international or leading Indian companies, the caste related identification has pretty much lost its importance.[324][325]
Family values are important in the Indian tradition, and multi-generational patriarchal joint families have been the norm in India, though nuclear families are becoming common in urban areas.[326] An overwhelming majority of Indians, with their consent, have their marriages arranged by their parents or other elders in the family.[327] Marriage is thought to be for life,[327] and the divorce rate is extremely low.[328] As of 2001, just 1.6 percent of Indian women were divorced, but this figure was rising due to their education and economic independence.[328]Child marriages are common, especially in rural areas; many women wed before reaching 18, which is their legal marriageable age.[329]Female infanticide and female foeticide in the country have caused a discrepancy in the sex ratio, as of 2005 it was estimated that there were 50 million more males than females in the nation.[330][331] However, a report from 2011 has shown improvement in the gender ratio.[332] The payment of dowry, although illegal, remains widespread across class lines.[333]Deaths resulting from dowry, mostly from bride burning, are on the rise, despite stringent anti-dowry laws.[334]
Many Indian festivals are religious in origin. The best known include Diwali, Ganesh Chaturthi, Thai Pongal, Holi, Durga Puja, Eid ul-Fitr, Bakr-Id, Christmas, and Vaisakhi.[335][336]Dragon age 2 download free full version deutsch.
Clothing
Cotton was domesticated in India by 4000 BCE. Traditional Indian dress varies in colour and style across regions and depends on various factors, including climate and faith. Popular styles of dress include draped garments such as the sari for women and the dhoti or lungi for men. Stitched clothes, such as the shalwar kameez for women and kurta–pyjama combinations or European-style trousers and shirts for men, are also popular.[337] Use of delicate jewellery, modelled on real flowers worn in ancient India, is part of a tradition dating back some 5,000 years; gemstones are also worn in India as talismans.[338]
Sports
In India, several traditional indigenous sports remain fairly popular, such as kabaddi, kho kho, pehlwani and gilli-danda. Some of the earliest forms of Asian martial arts, such as kalarippayattu, musti yuddha, silambam, and marma adi, originated in India. Chess, commonly held to have originated in India as chaturaṅga, is regaining widespread popularity with the rise in the number of Indian grandmasters.[339][340]Pachisi, from which parcheesi derives, was played on a giant marble court by Akbar.[341]
The improved results garnered by the Indian Davis Cup team and other Indian tennis players in the early 2010s have made tennis increasingly popular in the country.[342] India has a comparatively strong presence in shooting sports, and has won several medals at the Olympics, the World Shooting Championships, and the Commonwealth Games.[343][344] Other sports in which Indians have succeeded internationally include badminton[345] (Saina Nehwal and P V Sindhu are two of the top-ranked female badminton players in the world), boxing,[346] and wrestling.[347]Football is popular in West Bengal, Goa, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and the north-eastern states.[348]
Cricket is the most popular sport in India.[349] Major domestic competitions include the Indian Premier League, which is the most-watched cricket league in the world and ranks sixth among all sports leagues.[350]
India has hosted or co-hosted several international sporting events: the 1951 and 1982 Asian Games; the 1987, 1996, and 2011 Cricket World Cup tournaments; the 2003 Afro-Asian Games; the 2006 ICC Champions Trophy; the 2010 Hockey World Cup; the 2010 Commonwealth Games; and the 2017 FIFA U-17 World Cup. Major international sporting events held annually in India include the Chennai Open, the Mumbai Marathon, the Delhi Half Marathon, and the Indian Masters. The first Formula 1Indian Grand Prix featured in late 2011 but has been discontinued from the F1 season calendar since 2014.[351] India has traditionally been the dominant country at the South Asian Games. An example of this dominance is the basketball competition where the Indian team won three out of four tournaments to date.[352]
See also
Notes
- ^'[..] Jana Gana Mana is the National Anthem of India, subject to such alterations in the words as the Government may authorise as occasion arises; and the song Vande Mataram, which has played a historic part in the struggle for Indian freedom, shall be honoured equally with Jana Gana Mana and shall have equal status with it.' (Constituent Assembly of India 1950).
- ^According to Part XVII of the Constitution of India, Hindi in the Devanagari script is the official language of the Union, along with English as an additional official language.[5][1][6]States and union territories can have a different official language of their own other than Hindi or English.
- ^ abBesides specific religions, the last two categories in the 2011 Census were 'Other religions and persuasions' (0.65%) and 'Religion not stated' (0.23%).
- ^'The country's exact size is subject to debate because some borders are disputed. The Indian government lists the total area as 3,287,260 km2 (1,269,220 sq mi) and the total land area as 3,060,500 km2 (1,181,700 sq mi); the United Nations lists the total area as 3,287,263 km2 (1,269,219 sq mi) and total land area as 2,973,190 km2 (1,147,960 sq mi).' (Library of Congress 2004).
- ^See also: Names of India in its official languages.
- ^The Government of India also regards Afghanistan as a bordering country, as it considers all of Kashmir to be part of India. However, this is disputed, and the region bordering Afghanistan is administered by Pakistan. Source: 'Ministry of Home Affairs (Department of Border Management)'(PDF). Archived from the original(PDF) on 17 March 2015. Retrieved 1 September 2008.
- ^The northernmost point under Indian control is the disputed Siachen Glacier in Jammu and Kashmir; however, the Government of India regards the entire region of the former princely state of Jammu and Kashmir, including the Gilgit-Baltistan administered by Pakistan, to be its territory. It therefore assigns the latitude 37° 6' to its northernmost point.
- ^In 2015, the World Bank raised its international poverty line to $1.90 per day.[256]
References
- ^ abcdNational Informatics Centre 2005.
- ^ abc'National Symbols National Portal of India'. India.gov.in. Archived from the original on 4 February 2017. Retrieved 1 March 2017.
The National Anthem of India Jana Gana Mana, composed originally in Bengali by Rabindranath Tagore, was adopted in its Hindi version by the Constituent Assembly as the National Anthem of India on 24 January 1950.
- ^'National anthem of India: a brief on 'Jana Gana Mana''. News18. Archived from the original on 17 April 2019. Retrieved 7 June 2019.
- ^Wolpert 2003, p. 1.
- ^ abMinistry of Home Affairs 1960.
- ^ ab'Profile National Portal of India'. India.gov.in. Archived from the original on 30 August 2013. Retrieved 23 August 2013.
- ^'Constitutional Provisions – Official Language Related Part-17 of the Constitution of India'. National Informatics Centre (in Hindi). Archived from the original on 8 November 2016. Retrieved 1 December 2017.
- ^'Report of the Commissioner for linguistic minorities: 50th report (July 2012 to June 2013)'(PDF). Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities, Ministry of Minority Affairs, Government of India. Archived from the original(PDF) on 8 July 2016. Retrieved 26 December 2014.
- ^ abKhan, Saeed (25 January 2010). 'There's no national language in India: Gujarat High Court'. The Times of India. Archived from the original on 18 March 2014. Retrieved 5 May 2014.
- ^ ab'Learning with the Times: India doesn't have any 'national language''. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017.
- ^ abPress Trust of India (25 January 2010). 'Hindi, not a national language: Court'. The Hindu. Ahmedabad. Archived from the original on 4 July 2014. Retrieved 23 December 2014.
- ^ ab'C −1 Population by religious community – 2011'. Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner. Archived from the original on 25 August 2015. Retrieved 25 August 2015.
- ^ ab'World Population Prospects: The 2017 Revision'. ESA.UN.org (custom data acquired via website). United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 10 September 2017.
- ^'Population Enumeration Data (Final Population)'. Census of India. Archived from the original on 22 May 2016. Retrieved 17 June 2016.
- ^'A – 2 Decadal Variation in Population Since 1901'(PDF). Census of India. Archived(PDF) from the original on 30 April 2016. Retrieved 17 June 2016.
- ^ abcdefgh'World Economic Outlook Database, April 2019'. IMF.org. International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 9 April 2019.
- ^'Income Gini coefficient'. United Nations Development Program. Archived from the original on 23 July 2010. Retrieved 14 January 2017.
- ^'Human Development Indices and Indicators: 2018 Statistical update'(PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 15 September 2018. Retrieved 15 September 2018.
- ^ abcdClémentin-Ojha, Catherine (2014). ''India, that is Bharat…': One Country, Two Names'. South Asia Multidisciplinary Academic Journal. 10. Archived from the original on 28 September 2015.
- ^India, International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN), 2019 Quote: 'India, a megadiverse country with only 2.4% of the world's land area, accounts for 7-8% of all recorded species, including over 45,000 species of plants and 91,000 species of animals. The country’s diverse physical features and climatic conditions have resulted in a variety of ecosystems such as forests, wetlands, grasslands, desert, coastal and marine ecosystems which harbour and sustain high biodiversity.. Four of 34 globally identified biodiversity hotspots: The Himalayas, the Western Ghats, the North-East, and the Nicobar Islands, can be found in India.'
- ^Thieme, P. (1970), 'Sanskrit sindu-/Sindhu- and Old Iranian hindu-/Hindu-', in Mary Boyce; Ilya Gershevitch (eds.), W. B. Henning memorial volume, Lund Humphries, pp. 447–450
- ^Oxford English Dictionary.
- ^ abKuiper 2010, p. 86.
- ^Ministry of Law and Justice 2008.
- ^ abBarrow, Ian J. (2003). 'From Hindustan to India: Naming change in changing names'. South Asia: Journal of South Asian Studies. 26 (1): 37–49. doi:10.1080/085640032000063977.
- ^ abEncyclopædia Britannica.
- ^Petraglia, Allchin & 2007, p. 6.
- ^Singh 2009, pp. 89–93.
- ^ abConingham & Young 2015, pp. 104–105.
- ^Kulke & Rothermund 2004, pp. 21–23.
- ^ abSingh 2009, p. 181.
- ^Possehl 2003, p. 2.
- ^ abcSingh 2009, p. 255.
- ^ abSingh 2009, pp. 186–187.
- ^Witzel 2003, pp. 68–69.
- ^Kulke & Rothermund 2004, pp. 41–43.
- ^ abSingh 2009, pp. 250–251.
- ^Singh 2009, pp. 260–265.
- ^Kulke & Rothermund 2004, pp. 53–54.
- ^Singh 2009, pp. 312–313.
- ^Kulke & Rothermund 2004, pp. 54–56.
- ^Stein 1998, p. 21.
- ^Stein 1998, pp. 67–68.
- ^Singh 2009, p. 300.
- ^ abSingh 2009, p. 319.
- ^Stein 1998, pp. 78–79.
- ^Kulke & Rothermund 2004, p. 70.
- ^Singh 2009, p. 367.
- ^Kulke & Rothermund 2004, p. 63.
- ^Stein 1998, pp. 89–90.
- ^Singh 2009, pp. 408–415.
- ^Stein 1998, pp. 92–95.
- ^Kulke & Rothermund 2004, pp. 89–91.
- ^ abcSingh 2009, p. 545.
- ^Stein 1998, pp. 98–99.
- ^ abStein 1998, p. 132.
- ^ abcStein 1998, pp. 119–120.
- ^ abStein 1998, pp. 121–122.
- ^ abStein 1998, p. 123.
- ^ abStein 1998, p. 124.
- ^ abStein 1998, pp. 127–128.
- ^Ludden 2002, p. 68.
- ^Asher & Talbot 2008, p. 47.
- ^Metcalf & Metcalf 2006, p. 6.
- ^Ludden 2002, p. 67.
- ^Asher & Talbot 2008, pp. 50–51.
- ^ abAsher & Talbot 2008, p. 53.
- ^Metcalf & Metcalf 2006, p. 12.
- ^Robb 2001, p. 80.
- ^Stein 1998, p. 164.
- ^Asher & Talbot 2008, p. 115.
- ^Robb 2001, pp. 90–91.
- ^ abMetcalf & Metcalf 2006, p. 17.
- ^ abcAsher & Talbot 2008, p. 152.
- ^Asher & Talbot 2008, p. 158.
- ^Stein 1998, p. 169.
- ^Asher & Talbot 2008, p. 186.
- ^ abMetcalf & Metcalf 2006, pp. 23–24.
- ^Asher & Talbot 2008, p. 256.
- ^ abcAsher & Talbot 2008, p. 286.
- ^Metcalf & Metcalf 2006, pp. 44–49.
- ^Robb 2001, pp. 98–100.
- ^Ludden 2002, pp. 128–132.
- ^Metcalf & Metcalf 2006, pp. 51–55.
- ^Metcalf & Metcalf 2006, pp. 68–71.
- ^Asher & Talbot 2008, p. 289.
- ^Robb 2001, pp. 151–152.
- ^Metcalf & Metcalf 2006, pp. 94–99.
- ^Brown 1994, p. 83.
- ^Peers 2006, p. 50.
- ^Metcalf & Metcalf 2006, pp. 100–103.
- ^Brown 1994, pp. 85–86.
- ^Stein 1998, p. 239.
- ^Metcalf & Metcalf 2006, pp. 103–108.
- ^Robb 2001, p. 183.
- ^Sarkar 1983, pp. 1–4.
- ^Copland 2001, pp. ix–x.
- ^Metcalf & Metcalf 2006, p. 123.
- ^Stein 1998, p. 260.
- ^Bose & Jalal 2011, p. 117.
- ^Stein 1998, p. 258.
- ^ abMetcalf & Metcalf 2006, p. 126.
- ^ abMetcalf & Metcalf 2006, p. 97.
- ^Metcalf & Metcalf 2006, p. 163.
- ^Metcalf & Metcalf 2006, p. 167.
- ^Metcalf & Metcalf 2006, pp. 195–197.
- ^Metcalf & Metcalf 2006, p. 203.
- ^Metcalf & Metcalf 2006, p. 231.
- ^ abcMetcalf & Metcalf 2006, pp. 265–266.
- ^United States Department of Agriculture.
- ^Metcalf & Metcalf 2006, pp. 266–270.
- ^Metcalf & Metcalf 2006, p. 253.
- ^Metcalf & Metcalf 2006, p. 274.
- ^ abMetcalf & Metcalf 2006, pp. 247–248.
- ^Metcalf & Metcalf 2006, pp. 293–295.
- ^Metcalf & Metcalf 2006, p. 304.
- ^ abcdAli & Aitchison 2005.
- ^Dikshit & Schwartzberg, p. 7.
- ^Prakash et al. 2000.
- ^Dikshit & Schwartzberg, p. 11.
- ^Dikshit & Schwartzberg, p. 8.
- ^Dikshit & Schwartzberg, pp. 9–10.
- ^Ministry of Information and Broadcasting 2007, p. 1.
- ^ abKumar et al. 2006.
- ^Dikshit & Schwartzberg, p. 15.
- ^Duff 1993, p. 353.
- ^Dikshit & Schwartzberg, p. 16.
- ^Dikshit & Schwartzberg, p. 17.
- ^Dikshit & Schwartzberg, p. 12.
- ^Dikshit & Schwartzberg, p. 13.
- ^ abChang 1967, pp. 391–394.
- ^Posey 1994, p. 118.
- ^Wolpert 2003, p. 4.
- ^Heitzman & Worden 1996, p. 97.
- ^Conservation International 2007.
- ^Zoological Survey of India 2012, p. 1.
- ^ abPuri.
- ^Forest Survey of India 2013, pp. 11–14.
- ^Basak 1983, p. 24.
- ^ abTritsch 2001.
- ^Goyal, Anupam (2006), The WTO and International Environmental Law: Towards Conciliation, Oxford University Press, p. 295, ISBN978-0-19-567710-2 Quote: 'The Indian government successfully argued that the medicinal neem tree is part of traditional Indian knowledge. (page 295)'
- ^Hughes, Julie E. (2013), Animal Kingdoms, Harvard University Press, pp. 106–, ISBN978-0-674-07480-4 Quote: 'At same time, the leafy pipal trees and comparative abundance that marked the Mewari landscape fostered refinements unattainable in other lands.'
- ^Ameri, Marta; Costello, Sarah Kielt; Jamison, Gregg; Scott, Sarah Jarmer (2018), Seals and Sealing in the Ancient World: Case Studies from the Near East, Egypt, the Aegean, and South Asia, Cambridge University Press, pp. 156–7, ISBN978-1-108-17351-3 Quote: 'The last of the centaurs has the long, wavy, horizontal horns of a markhor, a human face, a heavy-set body that appears bovine, and a goat tail .. This figure is often depicted by itself, but it is also consistently represented in scenes that seem to reflect the adoration of a figure in a pipal tree or arbor and which may be termed ritual. These include fully detailed scenes like that visible in the large 'divine adoration' seal from Mohenjo-daro.'
- ^Paul Gwynne (2011), World Religions in Practice: A Comparative Introduction, John Wiley & Sons, p. 358, ISBN978-1-4443-6005-9 Quote: 'The tree under which Sakyamuni became the Buddha is a peepal tree (Ficus religiosa). page 358'
- ^Crame & Owen 2002, p. 142.
- ^Karanth 2006.
- ^Mace 1994, p. 4.
- ^Ministry of Environments and Forests 1972.
- ^Department of Environment and Forests 1988.
- ^Ministry of Environment and Forests.
- ^Secretariat of the Convention on Wetlands.
- ^United Nations Population Division.
- ^Burnell & Calvert 1999, p. 125.
- ^Election Commission of India.
- ^Saez, Lawrence; Sinha, Aseema (2010). 'Political cycles, political institutions and public expenditure in India, 1980–2000'. British Journal of Political Science. 40 (1): 91–113. doi:10.1017/s0007123409990226.
- ^Malik & Singh 1992, pp. 318–336.
- ^BBC 2012.
- ^Banerjee 2005, p. 3118.
- ^Sarkar 2007, p. 84.
- ^Chander 2004, p. 117.
- ^Bhambhri 1992, pp. 118, 143.
- ^The Hindu 2008.
- ^Dunleavy, Diwakar & Dunleavy 2007.
- ^Kulke & Rothermund 2004, p. 384.
- ^Business Standard 2009.
- ^'BJP first party since 1984 to win parliamentary majority on its own'. DNA. IANS. 16 May 2014. Archived from the original on 21 May 2014. Retrieved 20 May 2014.
- ^'Election commission'(PDF). eci.nic.in. 21 July 2017. Archived(PDF) from the original on 11 August 2017.
- ^'Oath'. India Today. Archived from the original on 21 July 2017.
- ^'Highlights: Ram Nath Kovind takes oath as India's 14th President'. The Indian Express. 25 July 2017. Archived from the original on 11 August 2017. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- ^Pylee, 2003 & a, p. 4.
- ^Dutt 1998, p. 421.
- ^Wheare 1980, p. 28.
- ^Echeverri-Gent 2002, pp. 19–20.
- ^Sinha 2004, p. 25.
- ^'In RTI reply, Centre says India has no national game'. 2 August 2012. Archived from the original on 4 August 2012. Retrieved 4 August 2012.
- ^'The Constitution of India'(PDF). Retrieved 16 July 2016.
- ^ abSharma 2007, p. 31.
- ^Sharma 2007, p. 138.
- ^Gledhill 1970, p. 112.
- ^ abSharma 1950.
- ^ abSharma 2007, p. 162.
- ^Mathew 2003, p. 524.
- ^Gledhill 1970, p. 127.
- ^Sharma 2007, p. 161.
- ^Sharma 2007, p. 143.
- ^Sharma 2007, p. 360.
- ^ abNeuborne 2003, p. 478.
- ^Sharma 2007, pp. 238, 255.
- ^Sripati 1998, pp. 423–424.
- ^Pylee, 2003 & b, p. 314.
- ^ abcdeLibrary of Congress 2004.
- ^Sharma 2007, p. 49.
- ^Rothermund 2000, pp. 48, 227.
- ^Gilbert 2002, pp. 486–487.
- ^Sharma 1999, p. 56.
- ^'No ties with Pakistan at India's cost, relations with New Delhi long-term: Russia India News'. Retrieved 14 October 2018.
- ^Alford 2008.
- ^'India and Latin America Trade – Economic Ties Latin America and India'. www.americasquarterly.org. Archived from the original on 25 May 2017. Retrieved 19 May 2017.
- ^Ghosh 2009, pp. 282–289.
- ^Sisodia & Naidu 2005, pp. 1–8.
- ^Perkovich 2001, pp. 60–86, 106–125.
- ^Kumar 2010.
- ^Nair 2007.
- ^Pandit 2009.
- ^ abThe Hindu 2011.
- ^Europa 2008.
- ^The Times of India 2008.
- ^British Broadcasting Corporation 2009.
- ^Rediff 2008 a.
- ^Reuters 2010.
- ^Curry 2010.
- ^ abcCentral Intelligence Agency.
- ^Behera 2011.
- ^Behera 2012.
- ^Stockholm International Peace Research Institute 2008, p. 178.
- ^ abMiglani 2011.
- ^Shukla 2011.
- ^Stockholm International Peace Research Initiative 2012.
- ^'Isro-Saarc satellite to be a communication vehicle'. Deccan Herald. Deccan Herald News Service. 12 January 2015. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ^'India Russia S-400 missile deal: All you need to know'. The Times of India. 5 October 2018. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ^International Monetary Fund 2011, p. 2.
- ^Nayak, Goldar & Agrawal 2010, p. xxv.
- ^International Monetary Fund.
- ^Wolpert 2003, p. xiv.
- ^ abcOrganisation for Economic Co-operation and Development 2007.
- ^Gargan 1992.
- ^Alamgir 2008, pp. 23, 97.
- ^WTO 1995.
- ^Sakib Sherani (17 April 2015). 'Pakistan's remittances'. dawn.com. Archived from the original on 16 December 2015. Retrieved 17 December 2015.
- ^The Times of India 2009.
- ^World Trade Organization 2010.
- ^Economist 2011.
- ^UN Comtrade (4 February 2015). 'India world's second largest textiles exporter'. TechCrunch. economictimes. Retrieved 2 June 2014.
- ^Bonner 2010.
- ^ abFarrell & Beinhocker 2007.
- ^Schwab 2010.
- ^Sheth 2009.
- ^'How Many People in India Pay Income Tax? Hardly Anyone'. 6 June 2013. Archived from the original on 31 December 2013.
- ^International Monetary Fund 2011.
- ^ abcPricewaterhouseCoopers 2011.
- ^World Bank 2010.
- ^'Measuring the cost of living worldwide'. The Economist. 21 March 2017. Archived from the original on 25 May 2017. Retrieved 25 May 2017.
- ^Telecom Regulatory Authority 2011.
- ^Khan, Danish (28 October 2017). 'Indian smartphone market grows 23% to overtake US in Q3; Samsung, Xiaomi drive shipments'. The Economic Times. Archived from the original on 31 October 2017. Retrieved 5 November 2017.
- ^Business Line 2010.
- ^Express India 2009.
- ^'India's total power capacity crosses 300 gw mark'. NDTV. Archived from the original on 16 June 2017.
- ^Nasscom 2011–2012.
- ^Vishal Dutta (10 July 2012). 'Indian biotech industry at critical juncture, global biotech stabilises: Report'. Economic Times. Retrieved 31 October 2012.
- ^'Indian pharmaceutical industry – growth story to continue'. Express Pharma. 15 January 2012. Archived from the original on 16 January 2013. Retrieved 31 October 2012.
- ^Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Sector in India: sector briefing by the UK Trade and Investment 2011, utki.gov.uk
- ^Yep 2011.
- ^'Differding Consulting Publi 6'. Differding.com. 11 February 2014. Archived from the original on 23 February 2014. Retrieved 4 April 2014.
- ^World Bank 2006.
- ^World Bank a.
- ^Kenny, Charles; Sandefur, Justin (7 October 2015). 'Why the World Bank is changing the definition of the word 'poor''. Vox. Archived from the original on 14 January 2017. Retrieved 26 February 2017.
- ^'Poverty headcount ratio at $1.90 a day (2011 PPP) (% of population)'. World Bank. Archived from the original on 15 February 2017. Retrieved 26 February 2017.
- ^'India's rank improves to 55th position on global hunger index'. India times. 13 October 2014.
- ^Internet Desk (28 May 2015). 'India is home to 194 million hungry people: UN'. The Hindu. Archived from the original on 2 December 2016.
- ^'India home to world's largest number of hungry people: report'. dawn.com. 29 May 2015. Archived from the original on 29 May 2015.
- ^Drèze & Goyal 2008, p. 46.
- ^'India – Global Slavery Index 2016'. Walk Free Foundation. Archived from the original on 3 May 2017. Retrieved 21 November 2017.
- ^'Bonded labourers, sex workers, forced beggars: India leads world in slavery'. 31 May 2016. Archived from the original on 1 October 2017. Retrieved 21 November 2017.
- ^'India ranks fourth in global slavery survey'. Times of India. 1 June 2016. Archived from the original on 1 October 2017. Retrieved 21 November 2017.
- ^'Child labour in India – ILO'(PDF). International Labour Organization. Archived(PDF) from the original on 1 December 2017. Retrieved 21 November 2017.
- ^Pal & Ghosh 2007.
- ^'India improves its ranking on corruption index'. 27 January 2016. Retrieved 21 November 2017.
- ^ abProvisional Population Totals, Census 2011, p. 160.
- ^ abProvisional Population Totals, Census 2011, p. 165.
- ^'Census Population'(PDF). Census of India. Ministry of Finance India. Archived from the original(PDF) on 26 August 2011. Retrieved 13 February 2013.
- ^Rorabacher 2010, pp. 35–39.
- ^World Health Organization 2006.
- ^Boston Analytics 2009.
- ^'Life expectancy in India'(PDF). newspaper. Times of India. Archived from the original on 21 September 2014.
- ^Dev & Rao 2009, p. 329.
- ^Garg 2005.
- ^Dyson & Visaria 2005, pp. 115–129.
- ^Ratna 2007, pp. 271–272.
- ^ abChandramouli 2011.
- ^'Urban Agglomerations/Cities having population 1 lakh and above'(PDF). Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. Archived(PDF) from the original on 17 October 2013. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- ^ abProvisional Population Totals, Census 2011, p. 163.
- ^Dharwadker 2010, pp. 168–194, 186.
- ^Ottenheimer 2008, p. 303.
- ^Mallikarjun 2004.
- ^Global Muslim population estimated at 1.57 billionArchived 1 June 2013 at the Wayback Machine. The Hindu (8 October 2009)
- ^'India Chapter Summary 2012'(PDF). Archived(PDF) from the original on 7 April 2014.
- ^Kuiper 2010, p. 15.
- ^ abHeehs 2002, pp. 2–5.
- ^Deutsch 1969, pp. 3, 78.
- ^Nakamura 1999.
- ^Kuiper 2010, pp. 296–329.
- ^Silverman 2007, p. 20.
- ^Kumar 2000, p. 5.
- ^Roberts 2004, p. 73.
- ^Lang & Moleski 2010, pp. 151–152.
- ^United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organisation.
- ^Chopra 2011, p. 46.
- ^Hoiberg & Ramchandani 2000.
- ^Johnson 2008.
- ^MacDonell 2004, pp. 1–40.
- ^Kālidāsa & Johnson 2001.
- ^Zvelebil 1997, p. 12.
- ^Hart 1975.
- ^Encyclopædia Britannica 2008.
- ^Ramanujan 1985, pp. ix–x.
- ^Das 2005.
- ^Datta 2006.
- ^Massey & Massey 1998.
- ^Encyclopædia Britannica b.
- ^Lal 2004, pp. 23, 30, 235.
- ^Karanth 2002, p. 26.
- ^'The Sunday Tribune – Spectrum'. www.tribuneindia.com. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 4 October 2017.
- ^Dissanayake & Gokulsing 2004.
- ^Rajadhyaksha & Willemen 1999, p. 652.
- ^The Economic Times.
- ^Sunetra Sen Narayan, Globalization and Television: A Study of the Indian Experience, 1990–2010 (Oxford University Press, 2015); 307 pages
- ^Kaminsky & Long 2011, pp. 684–692.
- ^Mehta 2008, pp. 1–10.
- ^Media Research Users Council 2012.
- ^Johnston, Bruce F. (1958). The Staple Food Economies of Western Tropical Africa. Stanford University Press. p. 14. ISBN978-0-8047-0537-0. Archived from the original on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 2 June 2012.
- ^Cornillez, Louise Marie M. (Spring 1999). 'The History of the Spice Trade in India'. Retrieved 18 February 2018.
- ^Schwartzberg 2011.
- ^'Spiritual Terrorism: Spiritual Abuse from the Womb to the Tomb', p. 391, by Boyd C. Purcell
- ^Messner 2009, p. 51-53.
- ^Messner 2012, p. 27-28.
- ^Makar 2007.
- ^ abMedora 2003.
- ^ abJones & Ramdas 2005, p. 111.
- ^Cullen-Dupont 2009, p. 96.
- ^Bunting 2011.
- ^Agnivesh 2005.
- ^Census of India-Gender CompositionArchived 13 November 2013 at the Wayback Machine 2011
- ^'Woman killed over dowry 'every hour' in India'. telegraph.com. 2 September 2013. Archived from the original on 23 March 2014. Retrieved 10 February 2014.
- ^'Rising number of dowry deaths in India:NCRB'. thehindu.com. 7 August 2013. Archived from the original on 7 February 2014. Retrieved 10 February 2014.
- ^Indian Festivals, archived from the original on 14 July 2016, retrieved 14 May 2016
- ^Popular India Festivals, archived from the original on 21 August 2011, retrieved 23 December 2007
- ^Tarlo 1996, pp. xii, xii, 11, 15, 28, 46.
- ^Eraly 2008, p. 160.
- ^Wolpert 2003, p. 2.
- ^Rediff 2008 b.
- ^Binmore 2007, p. 98.
- ^The Wall Street Journal 2009.
- ^British Broadcasting Corporation 2010 b.
- ^The Times of India 2010.
- ^British Broadcasting Corporation 2010 a.
- ^Mint 2010.
- ^Xavier 2010.
- ^Majumdar & Bandyopadhyay 2006, pp. 1–5.
- ^Shores, Lori (15 February 2007), Teens in India, Compass Point Books, p. 78, ISBN978-0-7565-2063-2, retrieved 24 July 2011
- ^'Top 10 most watched sports leagues in the world'. www.sportskeeda.com. 11 January 2016. Retrieved 14 May 2019.
- ^Dehejia 2011.
- ^'Basketball team named for 11th South Asian Games'. Nation.com.pk. 2 January 2010. Archived from the original on 2 December 2012. Retrieved 8 March 2013.
Bibliography
Overview
- 'India', The World Factbook, Central Intelligence Agency, retrieved 23 August 2017
- 'Country Profile: India'(PDF), Library of Congress Country Studies (5th ed.), Library of CongressFederal Research Division, December 2004, retrieved 30 September 2011
- Heitzman, J.; Worden, R. L. (August 1996), India: A Country Study, Area Handbook Series, Washington, D.C.: Library of Congress, ISBN978-0-8444-0833-0
- India, International Monetary Fund, retrieved 14 October 2011
- Provisional Population Totals, Paper 1 – Census 2011, Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, 2011, lay summary
- 'Constituent Assembly of India – Volume XII', Constituent Assembly of India: Debates, National Informatics Centre, Government of India, 24 January 1950, archived from the original on 21 July 2011, retrieved 17 July 2011
- There's No National Language in India: Gujarat High Court, The Times of India, 6 January 2007, retrieved 17 July 2011
- 'Table 1: Human Development Index and its Components'(PDF), Human Development Report 2011, United Nations, 2011
Etymology
- Serge Gruzinski (13 January 2015), The Eagle and the Dragon: Globalization and European Dreams of Conquest in China and America in the Sixteenth Century, John Wiley & Sons, ISBN978-0-7456-8134-4
- Hindustan, Encyclopædia Britannica, retrieved 17 July 2011
- Kaye, A. S. (1 September 1997), Phonologies of Asia and Africa, Eisenbrauns, ISBN978-1-57506-019-4
- Kuiper, K., ed. (July 2010), Culture of India, Rosen Publishing Group, ISBN978-1-61530-203-1
- Constitution of India(PDF), Ministry of Law and Justice, 29 July 2008, archived from the original(PDF) on 9 September 2014, retrieved 3 March 2012,
Article 1(1): 'India, that is Bharat, shall be a Union of States.'
- 'India', Oxford English Dictionary, Oxford University Press, retrieved 17 July 2011
History
- Asher, C. B.; Talbot, C (1 January 2008), India Before Europe (1st ed.), Cambridge University Press, ISBN978-0-521-51750-8
- Bose, S.; Jalal, A. (11 March 2011), Modern South Asia: History, Culture, Political Economy (3rd ed.), Routledge, ISBN978-0-415-77942-5
- Brown, J. M. (26 May 1994), Modern India: The Origins of an Asian Democracy, The Short Oxford History of the Modern World (2nd ed.), Oxford University Press, ISBN978-0-19-873113-9
- Coningham, Robin; Young, Ruth (2015), The Archaeology of South Asia: From the Indus to Asoka, c.6500 BCE–200 CE, Cambridge University Press, ISBN978-0-521-84697-4
- Copland, I. (8 October 2001), India 1885–1947: The Unmaking of an Empire (1st ed.), Longman, ISBN978-0-582-38173-5
- Kulke, H.; Rothermund, D. (1 August 2004), A History of India, 4th, Routledge, ISBN978-0-415-32920-0
- Ludden, D. (13 June 2002), India and South Asia: A Short History, One World, ISBN978-1-85168-237-9
- Metcalf, B.; Metcalf, T. R. (9 October 2006), A Concise History of Modern India (2nd ed.), Cambridge University Press, ISBN978-0-521-68225-1
- Peers, D. M. (3 August 2006), India under Colonial Rule 1700–1885 (1st ed.), Pearson Longman, ISBN978-0-582-31738-3
- Petraglia, Michael D.; Allchin, Bridget (2007), 'Human evolution and culture change in the Indian subcontinent', in Michael Petraglia; Bridget Allchin (eds.), The Evolution and History of Human Populations in South Asia: Inter-disciplinary Studies in Archaeology, Biological Anthropology, Linguistics and Genetics, Springer, ISBN978-1-4020-5562-1
- Possehl, G. (January 2003), The Indus Civilization: A Contemporary Perspective, Rowman Altamira, ISBN978-0-7591-0172-2
- Robb, P. (2001), A History of India, London: Palgrave, ISBN978-0-333-69129-8
- Sarkar, S. (1983), Modern India: 1885–1947, Delhi: Macmillan India, ISBN978-0-333-90425-1
- Singh, U. (2009), A History of Ancient and Medieval India: From the Stone Age to the 12th Century, Delhi: Longman, ISBN978-81-317-1677-9
- Sripati, V. (1998), 'Toward Fifty Years of Constitutionalism and Fundamental Rights in India: Looking Back to See Ahead (1950–2000)', American University International Law Review, 14 (2): 413–496
- Stein, B. (16 June 1998), A History of India (1st ed.), Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell, ISBN978-0-631-20546-3
- Stein, B. (27 April 2010), Arnold, D. (ed.), A History of India (2nd ed.), Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell, ISBN978-1-4051-9509-6
- 'Briefing Rooms: India', Economic Research Service, United States Department of Agriculture, 17 December 2009, archived from the original on 20 May 2011
- Thapar, Romila (2003), Penguin history of early India: from the origins to A.D.1300, Penguin Books, retrieved 13 February 2012
- Witzel, Michael (2001), 'Autochthonous Aryans? The Evidence from Old Indian and Iranian Texts'(PDF), Electronic Journal of Vedic Studies, 7 (3): 1–115
- Witzel, Michael (2003), 'Vedas and Upanișads', in Gavin D. Flood (ed.), The Blackwell companion to Hinduism, John Wiley & Sons, ISBN978-0-631-21535-6, retrieved 15 March 2012
- Witzel, Michael (2005), 'Indocentrism', in Bryant, Edwin; Patton, Laurie L. (eds.), TheE Indo-Aryan Controversy. Evidence and inference in Indian history, Routledge
- Wolpert, S. (25 December 2003), A New History of India (7th ed.), Oxford University Press, ISBN978-0-19-516678-1
Geography
- Ali, J. R.; Aitchison, J. C. (2005), 'Greater India', Earth-Science Reviews, 72 (3–4): 170–173, doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2005.07.005
- Chang, J. H. (1967), 'The Indian Summer Monsoon', Geographical Review, [American Geographical Society, Wiley], 57 (3), pp. 373–396, doi:10.2307/212640, JSTOR212640
- Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980 with Amendments Made in 1988(PDF), Department of Environment and Forests, Government of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, 1988, archived from the original(PDF) on 21 July 2011, retrieved 25 July 2011
- Dikshit, K. R.; Schwartzberg, Joseph E., 'India: Land', Encyclopædia Britannica, pp. 1–29
- Duff, D. (29 October 1993), Holmes Principles of Physical Geology (4th ed.), Routledge, ISBN978-0-7487-4381-0
- Kumar, V. S.; Pathak, K. C.; Pednekar, P.; Raju, N. S. N. (2006), 'Coastal processes along the Indian coastline'(PDF), Current Science, 91 (4), pp. 530–536, archived from the original(PDF) on 8 September 2009
- India Yearbook 2007, New Delhi: Publications Division, Ministry of Information and Broadcasting, Government of India, 2007, ISBN978-81-230-1423-4
- Posey, C. A. (1 November 1994), The Living Earth Book of Wind and Weather, Reader's Digest, ISBN978-0-89577-625-9
- Prakash, B.; Kumar, S.; Rao, M. S.; Giri, S. C. (2000), 'Holocene Tectonic Movements and Stress Field in the Western Gangetic Plains'(PDF), Current Science, 79 (4): 438–449
Biodiversity
- Ali, S.; Ripley, S. D.; Dick, J. H. (15 August 1996), A Pictorial Guide to the Birds of the Indian Subcontinent (2nd ed.), Mumbai: Oxford University Press, ISBN978-0-19-563732-8
- Animal Discoveries 2011: New Species and New Records(PDF), Zoological Survey of India, 2012, archived from the original(PDF) on 16 January 2013, retrieved 20 July 2012
- Basak, R. K. (1983), Botanical Survey of India: Account of Its Establishment, Development, and Activities, retrieved 20 July 2011
- 'Hotspots by Region', Biodiversity Hotspots, Conservation International, 2007, archived from the original on 8 July 2007, retrieved 28 February 2011
- Crame, J. A.; Owen, A. W. (1 August 2002), Palaeobiogeography and Biodiversity Change: The Ordovician and Mesozoic–Cenozoic Radiations, Geological Society Special Publication (194), Geological Society of London, ISBN978-1-86239-106-2, retrieved 8 December 2011
- 'Forest Cover'(PDF). State of Forest Report 2013. Dehradun: Forest Survey of India. 2013.
- Griffiths, M. (6 July 2010), The Lotus Quest: In Search of the Sacred Flower, St. Martin's Press, ISBN978-0-312-64148-1
- Karanth, K. P. (25 March 2006), 'Out-of-India Gondwanan Origin of Some Tropical Asian Biota'(PDF), Current Science, 90 (6): 789–792, retrieved 18 May 2011
- Mace, G. M. (March 1994), '1994 IUCN Red List of Threatened Animals', World Conservation Monitoring Centre, International Union for Conservation of Nature, ISBN978-2-8317-0194-3
- 'Biosphere Reserves of India', C. P. R. Environment Education Centre, Ministry of Environment and Forests, Government of India, retrieved 17 July 2011
- Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, Ministry of Environments and Forests, Government of India, 9 September 1972, retrieved 25 July 2011
- Puri, S. K., Biodiversity Profile of India, archived from the original on 21 November 2011, retrieved 20 June 2007
- The List of Wetlands of International Importance(PDF), The Secretariat of the Convention on Wetlands, 4 June 2007, p. 18, archived from the original(PDF) on 21 June 2007, retrieved 20 June 2007
- Tritsch, M. F. (3 September 2001), Wildlife of India, London: HarperCollins, ISBN978-0-00-711062-9
Politics
- Banerjee, Sumanta (16–22 July 2005). 'Civilising the BJP'. Economic & Political Weekly. 40 (29): 3116–3119. JSTOR4416896.
- Bhambhri, C. P. (1 May 1992), Politics in India, 1991–1992, Shipra, ISBN978-81-85402-17-8, retrieved 20 July 2011
- Burnell, P. J.; Calvert, P. (1 May 1999), The Resilience of Democracy: Persistent Practice, Durable Idea (1st ed.), Taylor & Francis, ISBN978-0-7146-8026-2, retrieved 20 July 2011
- India, Press Trust of (16 May 2009), 'Second UPA Win, A Crowning Glory for Sonia's Ascendancy', Business Standard India, Business Standard, retrieved 13 June 2009
- Chander, N. J. (1 January 2004), Coalition Politics: The Indian Experience, Concept Publishing Company, ISBN978-81-8069-092-1, retrieved 20 July 2011
- Dunleavy, P.; Diwakar, R.; Dunleavy, C. (2007), The Effective Space of Party Competition(PDF) (5), London School of Economics and Political Science, retrieved 27 September 2011
- Dutt, S. (1998), 'Identities and the Indian State: An Overview', Third World Quarterly, 19 (3): 411–434, doi:10.1080/01436599814325
- Echeverri-Gent, J. (January 2002), 'Politics in India's Decentred Polity', in Ayres, A.; Oldenburg, P. (eds.), Quickening the Pace of Change, India Briefing, London: M. E. Sharpe, pp. 19–53, ISBN978-0-7656-0812-3
- 'Current Recognised Parties'(PDF), Election Commission of India, 14 March 2009, retrieved 5 July 2010
- Gledhill, A. (30 March 1970), The Republic of India: The Development of its Laws and Constitution, Greenwood, ISBN978-0-8371-2813-9, retrieved 21 July 2011
- Halarnkar, Samar (13 June 2012). 'Narendra Modi makes his move'. BBC News.
The right-wing Hindu nationalist Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), India's primary opposition party
- Narasimha Rao Passes Away, The Hindu, 24 December 2004, retrieved 2 November 2008
- Malik, Yogendra K.; Singh, V.B. (April 1992). 'Bharatiya Janata Party: An Alternative to the Congress (I)?'. Asian Survey. 32 (4): 318–336. doi:10.2307/2645149. JSTOR2645149.
- Mathew, K. M. (1 January 2003), Manorama Yearbook, Malayala Manorama, ISBN978-81-900461-8-3, retrieved 21 July 2011
- 'National Symbols of India', Know India, National Informatics Centre, Government of India, retrieved 27 September 2009
- Neuborne, B. (2003), 'The Supreme Court of India', International Journal of Constitutional Law, 1 (1): 476–510, doi:10.1093/icon/1.3.476
- Pylee, M. V. (2003), 'The Longest Constitutional Document', Constitutional Government in India (2nd ed.), S. Chand, ISBN978-81-219-2203-6
- Pylee, M. V. (2003), 'The Union Judiciary: The Supreme Court', Constitutional Government in India (2nd ed.), S. Chand, ISBN978-81-219-2203-6, retrieved 2 November 2007
- Sarkar, N. I. (1 January 2007), Sonia Gandhi: Tryst with India, Atlantic, ISBN978-81-269-0744-1, retrieved 20 July 2011
- Sharma, R. (1950), 'Cabinet Government in India', Parliamentary Affairs, 4 (1): 116–126
- Sharma, B. K. (August 2007), Introduction to the Constitution of India (4th ed.), Prentice Hall, ISBN978-81-203-3246-1
- Sinha, A. (2004), 'The Changing Political Economy of Federalism in India', India Review, 3 (1): 25–63, doi:10.1080/14736480490443085
- World's Largest Democracy to Reach One Billion Persons on Independence Day, United NationsPopulation Division, retrieved 5 October 2011
- Wheare, K. C. (June 1980), Federal Government (4th ed.), Oxford University Press, ISBN978-0-313-22702-8
Foreign relations and military
- Alford, P. (7 July 2008), G8 Plus 5 Equals Power Shift, The Australian, retrieved 21 November 2009
- Behera, L. K. (7 March 2011), Budgeting for India's Defence: An Analysis of Defence Budget 2011–2012, Institute for Defence Studies and Analyses, retrieved 4 April 2011
- Behera, L. K. (20 March 2012), India's Defence Budget 2012–13, Institute for Defence Studies and Analyses, archived from the original on 15 December 2012, retrieved 26 March 2012
- 'Russia Agrees India Nuclear Deal', BBC News, British Broadcasting Corporation, 11 February 2009, retrieved 22 August 2010
- Curry, B. (27 June 2010), Canada Signs Nuclear Deal with India, The Globe and Mail, retrieved 13 May 2011
- 'India, Europe Strategic Relations', Europa: Summaries of EU Legislation, European Union, 8 April 2008, retrieved 14 January 2011
- Ghosh, A. (1 September 2009), India's Foreign Policy, Pearson, ISBN978-81-317-1025-8
- Gilbert, M. (17 December 2002), A History of the Twentieth Century, William Morrow, ISBN978-0-06-050594-3, retrieved 22 July 2011
- 'India, Russia Review Defence Ties', The Hindu, The Hindu, 5 October 2009, retrieved 8 October 2011
- Kumar, A. V. (1 May 2010), 'Reforming the NPT to Include India', Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists, retrieved 1 November 2010
- Miglani, S. (28 February 2011), 'With An Eye on China, India Steps Up Defence Spending', Reuters, retrieved 6 July 2011
- Nair, V. K. (2007), No More Ambiguity: India's Nuclear Policy(PDF), archived from the original(PDF) on 27 September 2007, retrieved 7 June 2007
- Pandit, R. (27 July 2009), N-Submarine to Give India Crucial Third Leg of Nuke Triad, The Times of India, retrieved 10 March 2010
- Perkovich, G. (5 November 2001), India's Nuclear Bomb: The Impact on Global Proliferation, University of California Press, ISBN978-0-520-23210-5, retrieved 22 July 2011
- India, France Agree on Civil Nuclear Cooperation, Rediff, 25 January 2008, retrieved 22 August 2010
- 'UK, India Sign Civil Nuclear Accord', Reuters, 13 February 2010, retrieved 22 August 2010
- Ripsman, N. M.; Paul, T. V. (18 March 2010), Globalization and the National Security State, Oxford University Press, ISBN978-0-19-539390-3, retrieved 22 July 2011
- Rothermund, D. (17 October 2000), The Routledge Companion to Decolonization, Routledge Companions to History (1st ed.), Routledge, ISBN978-0-415-35632-9
- India Gets Its First Homegrown Fighter Jet, RIA Novosti, 10 January 2011, retrieved 1 April 2009
- Sharma, S. R. (1 January 1999), India–USSR Relations 1947–1971: From Ambivalence to Steadfastness, 1, Discovery, ISBN978-81-7141-486-4
- Shukla, A. (5 March 2011), 'China Matches India's Expansion in Military Spending', Business Standard India, Business Standard, retrieved 6 July 2011
- Sisodia, N. S.; Naidu, G. V. C. (2005), Changing Security Dynamic in Eastern Asia: Focus on Japan, Promilla, ISBN978-81-86019-52-8
- 'SIPRI Yearbook 2008: Armaments, Disarmament, and International Security', Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, Oxford University Press, 8 August 2008, ISBN978-0-19-954895-8, retrieved 22 July 2011
- 'Rise in international arms transfers is driven by Asian demand, says SIPRI', Stockholm International Peace Research Initiative, 19 March 2012, retrieved 5 April 2016
- India, US Sign 123 Agreement, The Times of India, 11 October 2008, retrieved 21 July 2011
Economy
- Alamgir, J. (24 December 2008), India's Open-Economy Policy: Globalism, Rivalry, Continuity, Taylor & Francis, ISBN978-0-415-77684-4, retrieved 23 July 2011
- Bonner, B (20 March 2010), 'Make Way, World. India Is on the Move', Christian Science Monitor, retrieved 23 July 2011
- 'India Lost $462bn in Illegal Capital Flows, Says Report', BBC News, British Broadcasting Corporation, 18 November 2010, retrieved 23 July 2011
- 'India Second Fastest Growing Auto Market After China', Business Line, 9 April 2010, retrieved 23 July 2011
- Drèze, Jean; Sen, Amartya (2013), An Uncertain Glory: India and Its Contradictions, Allen Lane
- 'India's Economy: Not Just Rubies and Polyester Shirts', The Economist, 8 October 2011, retrieved 9 October 2011
- 'Indian Car Exports Surge 36%', Express India, 13 October 2009, retrieved 5 April 2016
- Report for Selected Countries and Subjects: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, Nepal, Pakistan, Philippines, Sri Lanka, Thailand, International Monetary Fund, April 2011, retrieved 23 July 2011
- Farrell, D.; Beinhocker, E. (19 May 2007), Next Big Spenders: India's Middle Class, McKinsey & Company, retrieved 17 September 2011
- Gargan, E. A. (15 August 1992), 'India Stumbles in Rush to a Free Market Economy', The New York Times, retrieved 22 July 2011
- World Economic Outlook Update(PDF), International Monetary Fund, June 2011, retrieved 22 July 2011
- Nayak, P. B.; Goldar, B.; Agrawal, P. (10 November 2010), India's Economy and Growth: Essays in Honour of V. K. R. V. Rao, SAGE Publications, ISBN978-81-321-0452-0
- Economic Survey of India 2007: Policy Brief(PDF), Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, October 2007, archived from the original(PDF) on 6 June 2011, retrieved 22 July 2011
- Pal, P.; Ghosh, J (July 2007), 'Inequality in India: A Survey of Recent Trends'(PDF), Economic and Social Affairs: DESA Working Paper No. 45, United Nations, retrieved 23 July 2011
- PricewaterhouseCoopers (January 2011), The World in 2050: The Accelerating Shift of Global Economic Power: Challenges and Opportunities(PDF), retrieved 23 July 2011
- Schwab, K. (2010), The Global Competitiveness Report 2010–2011(PDF), World Economic Forum, retrieved 10 May 2011
- Sheth, N. (28 May 2009), 'Outlook for Outsourcing Spending Brightens', The Wall Street Journal, retrieved 3 October 2010
- Srivastava, V. C. (2008), 'Introduction', in V.C. Srivastava; Lallanji Gopal; D.P. Chattopadhyaya (eds.), History of Agriculture in India (p to c 1200 AD), History of Science, Philosophy and Culture in Indian Civization, V (Part 1), Concept Publishing Co, ISBN978-81-8069-521-6
- Information Note to the Press (Press Release No.29 /2011)(PDF), Telecom Regulatory Authority of India, 6 April 2011, archived from the original(PDF) on 24 April 2011, retrieved 23 July 2011
- Exporters Get Wider Market Reach, The Times of India, 28 August 2009, retrieved 23 July 2011
- Corruption Perception Index 2010 – India Continues to be Corrupt(PDF), Transparency International, 26 October 2011, archived from the original(PDF) on 28 July 2011, retrieved 23 July 2011
- New Global Poverty Estimates – What It Means for India, World Bank, retrieved 23 July 2011
- 'India: Undernourished Children – A Call for Reform and Action', World Bank, retrieved 23 July 2011
- Inclusive Growth and Service Delivery: Building on India's Success(PDF), World Bank, 29 May 2006, retrieved 7 May 2009
- India Country Overview September 2010, World Bank, September 2010, retrieved 23 July 2011
- Trade to Expand by 9.5% in 2010 After a Dismal 2009, WTO Reports, World Trade Organization, 26 March 2010, retrieved 23 July 2011
- Yep, E. (27 September 2011), 'ReNew Wind Power Gets $201 Million Goldman Investment', Wall Street Journal, The Wall Street Journal, retrieved 27 September 2011
- Indian IT-BPO Industry, NASSCOM, 2011–2012, archived from the original on 9 May 2012, retrieved 22 June 2012
- UNDERSTANDING THE WTO: THE ORGANIZATION Members and Observers, WTO, 1995, archived from the original on 17 January 2010, retrieved 23 June 2012
Demographics
- Bonner, A. (1990), Averting the Apocalypse: Social Movements in India Today, Duke University Press, ISBN978-0-8223-1048-8, retrieved 24 July 2011
- Healthcare in India: Report Highlights(PDF), Boston Analytics, January 2009, archived from the original(PDF) on 28 July 2011, retrieved 23 July 2011
- Dev, S. M.; Rao, N. C. (2009), India: Perspectives on Equitable Development, Academic Foundation, ISBN978-81-7188-685-2
- Dharwadker, A. (28 October 2010), 'Representing India's Pasts: Time, Culture, and Problems of Performance Historiography', in Canning, C. M.; Postlewait, T. (eds.), Representing the Past: Essays in Performance Historiography, University of Iowa Press, ISBN978-1-58729-905-6, retrieved 24 July 2011
- Drèze, J.; Goyal, A. (9 February 2009), 'The Future of Mid-Day Meals', in Baru, R. V. (ed.), School Health Services in India: The Social and Economic Contexts, SAGE Publications, ISBN978-81-7829-873-3
- Dyson, T.; Visaria, P. (7 July 2005), 'Migration and Urbanisation: Retrospect and Prospects', in Dyson, T.; Casses, R.; Visaria, L. (eds.), Twenty-First Century India: Population, Economy, Human Development, and the Environment, Oxford University Press, ISBN978-0-19-928382-8
- Garg, S. C. (19 April 2005), Mobilizing Urban Infrastructure Finance in India(PDF), World Bank, retrieved 27 January 2010
- Mallikarjun, B (November 2004), 'Fifty Years of Language Planning for Modern Hindi – The Official Language of India', Language in India, 4 (11), ISSN1930-2940, retrieved 24 July 2011
- Notification No. 2/8/60-O.L, Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India, 27 April 1960, archived from the original on 1 October 2014, retrieved 13 May 2011
- 'Religious Composition', Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India, 2010–2011, retrieved 23 July 2011
- 'Census Data 2001', Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India, 2010–2011, retrieved 22 July 2011
- Ottenheimer, H. J. (2008), The Anthropology of Language: An Introduction to Linguistic Anthropology, Cengage, ISBN978-0-495-50884-7
- Ratna, U. (2007), 'Interface Between Urban and Rural Development in India', in Dutt, A. K.; Thakur, B (eds.), City, Society, and Planning, 1, Concept, ISBN978-81-8069-459-2
- Robinson, S. (1 May 2008), 'India's Medical Emergency', Time, retrieved 23 July 2011
- Rorabacher, J. A. (2010), Hunger and Poverty in South Asia, Gyan, ISBN978-81-212-1027-0
- Country Cooperation Strategy: India(PDF), World Health Organization, November 2006, retrieved 23 July 2011
- Chandramouli, C. (15 July 2011), Rural Urban Distribution of Population(PDF), Ministry of Home Affairs (India), retrieved 24 January 2015
Culture
- Agnivesh, Swami; Rama Mani; Angelika Köster-Lossack (25 November 2005). 'Missing: 50 million Indian girls'. New York Times. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- Bunting, Madeleine (22 July 2011). 'India's missing women'. The Guardian. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- Binmore, K. G. (27 March 2007), Playing for Real: A Text on Game Theory, Oxford University Press, ISBN978-0-19-530057-4
- Bladholm, L. (12 August 2000), The Indian Grocery Store Demystified (1st ed.), Macmillan Publishers, ISBN978-1-58063-143-3
- 'Saina Nehwal: India's Badminton Star and 'New Woman'', BBC News, 1 August 2010, retrieved 5 October 2010
- 'Commonwealth Games 2010: India Dominate Shooting Medals', BBC News, 7 October 2010, retrieved 3 June 2011
- Chopra, P. (18 March 2011), A Joint Enterprise: Indian Elites and the Making of British Bombay, University of Minnesota Press, ISBN978-0-8166-7037-6
- Cullen-Dupont, K. (July 2009), Human Trafficking (1st ed.), Infobase Publishing, ISBN978-0-8160-7545-4
- Das, S. K. (1 January 2005), A History of Indian Literature, 500–1399: From Courtly to the Popular, Sahitya Akademi, ISBN978-81-260-2171-0
- Datta, A. (2006), The Encyclopaedia of Indian Literature, 2, Sahitya Akademi, ISBN978-81-260-1194-0
- Dehejia, R. S. (7 November 2011), 'Indian Grand Prix Vs. Encephalitis?', The Wall Street Journal, retrieved 20 December 2011
- Deutsch, E. (30 April 1969), Advaita Vedānta: A Philosophical Reconstruction, University of Hawaii Press, ISBN978-0-8248-0271-4
- Dissanayake, W. K.; Gokulsing, M. (May 2004), Indian Popular Cinema: A Narrative of Cultural Change (2nd ed.), Trentham Books, ISBN978-1-85856-329-9
- Southern Movies Account for over 75% of Film Revenues, The Economic Times, 18 November 2009, retrieved 18 June 2011
- 'South Asian Arts: Indian Dance', Encyclopædia Britannica, retrieved 17 July 2011
- 'Tamil Literature', Encyclopædia Britannica, 2008, retrieved 24 July 2011
- Eraly, A. (2008), India, Penguin Books, ISBN978-0-7566-4952-4, retrieved 24 July 2011
- Hart, G. L. (August 1975), Poems of Ancient Tamil: Their Milieu and Their Sanskrit Counterparts (1st ed.), University of California Press, ISBN978-0-520-02672-8
- Heehs, P., ed. (1 September 2002), Indian Religions: A Historical Reader of Spiritual Expression and Experience, New York University Press, ISBN978-0-8147-3650-0, retrieved 24 July 2011
- Henderson, C. E. (2002), Culture and Customs of India, Greenwood Publishing Group, ISBN978-0-313-30513-9
- Hoiberg, D.; Ramchandani, I. (2000), Students' Britannica India: Select Essays, Popular Prakashan, ISBN978-0-85229-762-9
- Johnson, W. J., ed. (1 September 2008), The Sauptikaparvan of the Mahabharata: The Massacre at Night, Oxford World's Classics (2nd ed.), Oxford University Press, ISBN978-0-19-282361-8
- Jones, G.; Ramdas, K. (2005), (Un)tying the Knot: Ideal and Reality in Asian Marriage, National University of Singapore Press, ISBN978-981-05-1428-0
- Kālidāsa; Johnson, W. J. (15 November 2001), The Recognition of Śakuntalā: A Play in Seven Acts, Oxford University Press, ISBN978-0-19-283911-4
- Kaminsky, Arnold P.; Long, Roger D. (30 September 2011), India Today: An Encyclopedia of Life in the Republic: An Encyclopedia of Life in the Republic, ABC-CLIO, ISBN978-0-313-37462-3, retrieved 12 September 2012
- Karanth, S. K. (October 2002), Yakṣagāna, Abhinav Publications, ISBN978-81-7017-357-1
- Kiple, K. F.; Ornelas, K. C., eds. (2000), The Cambridge World History of Food, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN978-0-521-40216-3
- Kuiper, K., ed. (1 July 2010), The Culture of India, Britannica Educational Publishing, ISBN978-1-61530-203-1, retrieved 24 July 2011
- Kumar, V. (January 2000), Vastushastra, All You Wanted to Know About Series (2nd ed.), Sterling Publishing, ISBN978-81-207-2199-9
- Lal, A. (2004), The Oxford Companion to Indian Theatre, Oxford University Press, ISBN978-0-19-564446-3, retrieved 24 July 2011
- Lang, J.; Moleski, W. (1 December 2010), Functionalism Revisited, Ashgate Publishing, ISBN978-1-4094-0701-0
- MacDonell, A. A. (2004), A History of Sanskrit Literature, Kessinger Publishing, ISBN978-1-4179-0619-2
- Majumdar, B.; Bandyopadhyay, K. (2006), A Social History of Indian Football: Striving To Score, Routledge, ISBN978-0-415-34835-5
- Makar, E. M. (2007), An American's Guide to Doing Business in India, Adams, ISBN978-1-59869-211-2
- Massey, R.; Massey, J (1998), The Music of India, Abhinav Publications, ISBN978-81-7017-332-8
- Medora, N. (2003), 'Mate Selection in Contemporary India: Love Marriages Versus Arranged Marriages', in Hamon, R. R.; Ingoldsby, B. B. (eds.), Mate Selection Across Cultures, SAGE Publications, pp. 209–230, ISBN978-0-7619-2592-7
- Messner, W. (2009), Working with India. The Softer Aspects of a Successful Collaboration with the Indian IT & BPO Industry, Springer, ISBN978-3-540-89077-5
- Messner, W. (2012), Engaging with India. How to Manage the Softer Aspects of a Global Collaboration, Createspace, ISBN978-1-4662-4490-0
- 'Indian Readership Survey 2012 Q1 : Topline Findings'(PDF). Media Research Users Council. Growth: Literacy & Media Consumption. Archived from the original(PDF) on 7 April 2014. Retrieved 12 September 2012.
- Mehta, Nalin (30 July 2008), Television in India: Satellites, Politics and Cultural Change, Taylor & Francis US, ISBN978-0-415-44759-1, retrieved 12 September 2012
- Is Boxing the New Cricket?, Mint, 24 September 2010, retrieved 5 October 2010
- Nakamura, H. (1 April 1999), Indian Buddhism: A Survey with Bibliographical Notes, Buddhist Tradition Series (12th ed.), Motilal Banarsidass, ISBN978-81-208-0272-8
- Puskar-Pasewicz, M. (16 September 2010), Cultural Encyclopedia of Vegetarianism, Greenwood Publishing Group, ISBN978-0-313-37556-9
- Raghavan, S. (23 October 2006), Handbook of Spices, Seasonings, and Flavorings (2nd ed.), CRC Press, ISBN978-0-8493-2842-8
- Raichlen, S. (10 May 2011), 'A Tandoor Oven Brings India's Heat to the Backyard', The New York Times, retrieved 14 June 2011
- Rajadhyaksha, A.; Willemen, P., eds. (22 January 1999), Encyclopaedia of Indian Cinema (2nd ed.), British Film Institute, ISBN978-0-85170-669-6
- Ramanujan, A. K. (translator) (15 October 1985), Poems of Love and War: From the Eight Anthologies and the Ten Long Poems of Classical Tamil, New York: Columbia University Press, pp. ix–x, ISBN978-0-231-05107-1
- Rawat, Ramnarayan S (23 March 2011), Reconsidering Untouchability: Chamars and Dalit History in North India, Indiana University Press, ISBN978-0-253-22262-6
- Anand Crowned World Champion, Rediff, 29 October 2008, retrieved 29 October 2008
- Roberts, N. W. (12 July 2004), Building Type Basics for Places of Worship (1st ed.), John Wiley & Sons, ISBN978-0-471-22568-3
- Schoenhals, M. (22 November 2003), Intimate Exclusion: Race and Caste Turned Inside Out, University Press of America, ISBN978-0-7618-2697-2
- Schwartzberg, J. (2011), 'India: Caste', Encyclopædia Britannica, retrieved 17 July 2011
- Sen, A. (5 September 2006), The Argumentative Indian: Writings on Indian History, Culture, and Identity (1st ed.), Picador, ISBN978-0-312-42602-6
- Seymour, S.C. (28 January 1999), Women, Family, and Child Care in India: A World in Transition, Cambridge University Press, ISBN978-0-521-59884-2
- Silverman, S. (10 October 2007), Vastu: Transcendental Home Design in Harmony with Nature, Gibbs Smith, ISBN978-1-4236-0132-6
- Tarlo, E. (1 September 1996), Clothing Matters: Dress and Identity in India (1st ed.), University of Chicago Press, ISBN978-0-226-78976-7, retrieved 24 July 2011
- Sawant Shoots Historic Gold at World Championships, The Times of India, 9 August 2010, retrieved 25 May 2011
- Taj Mahal, United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organisation, retrieved 3 March 2012
- India Aims for Center Court, The Wall Street Journal, 11 September 2009, retrieved 29 September 2010
- Wengell, D. L.; Gabriel, N. (1 September 2008), Educational Opportunities in Integrative Medicine: The A-to-Z Healing Arts Guide and Professional Resource Directory (1st ed.), The Hunter Press, ISBN978-0-9776552-4-3
- Intergenerational Mobility for Dalits Is Visible, Albeit Limited(PDF). World Bank Report 2011. 2011. doi:10.1596/978-0-8213-8689-7. ISBN978-0-8213-8689-7. Retrieved 6 September 2012.
- Xavier, L. (12 September 2010), Sushil Kumar Wins Gold in World Wrestling Championship, The Times of India, retrieved 5 October 2010
- Yadav, S. S.; McNeil, D.; Stevenson, P. C. (23 October 2007), Lentil: An Ancient Crop for Modern Times, Springer, ISBN978-1-4020-6312-1
- Zvelebil, K. V. (1 August 1997), Companion Studies to the History of Tamil Literature, Brill Publishers, ISBN978-90-04-09365-2
External links
Government
General information
- 'India'. The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency.
- India at Curlie
- India from UCB Libraries GovPubs
- India from the BBC News
- Geographic data related to India at OpenStreetMap
- Key Development Forecasts for India from International Futures
Coordinates: 21°N78°E / 21°N 78°E
| States and union territories of India | |
|---|---|
Map | |
| Category | Federated states |
| Location | Republic of India |
| Number | 29 States 7 Union territories |
| Populations | States: Sikkim - 610,577(lowest); Uttar Pradesh - 199,812,341(highest) Union Territories: Lakshadweep - 64,473 (lowest); Delhi - 16,787,941 (highest) |
| Areas | States: 3,702 km2 (1,429 sq mi) Goa – 342,269 km2 (132,151 sq mi) Rajasthan Union territories: 32 km2 (12 sq mi) Lakshadweep – 8,249 km2 (3,185 sq mi) Andaman and Nicobar Islands |
| Government | State governments, Union Government (Union territories) |
| Subdivisions | Districts, Divisions |
India is a federal union comprising 29 states and 7 union territories, for a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions.
| States and union territories of India ordered by |
|---|
|
- 2History
- 3List
Responsibilities and authorities[edit]
The Constitution of India distributes the sovereign executive and legislative powers exercisable with respect to the territory of any State between the Union and that State.[1]
History[edit]
Pre-independence[edit]
The Indian subcontinent has been ruled by many different ethnic groups throughout its history, each instituting their own policies of administrative division in the region.[2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11][excessive citations] During the British Raj, the original administrative structure was mostly kept, and India was divided into provinces (also called Presidencies) that were directly governed by the British and princely states which were nominally controlled by a local prince or raja loyal to the British Empire, which held de facto sovereignty (suzerainty) over the princely states.
1947–1950[edit]
Between 1947 and 1950 the territories of the princely states were politically integrated into the Indian Union. Most were merged into existing provinces; others were organised into new provinces, such as Rajputana, Himachal Pradesh, Madhya Bharat, and Vindhya Pradesh, made up of multiple princely states; a few, including Mysore, Hyderabad, Bhopal, and Bilaspur, became separate provinces. The new Constitution of India, which came into force on 26 January 1950, made India a sovereign democratic republic. The new republic was also declared to be a 'Union of States'.[12] The constitution of 1950 distinguished between three main types of states:[citation needed]
- Part A states, which were the former governors' provinces of British India, were ruled by an elected governor and state legislature. The nine Part A states were Assam, Bihar, Bombay, Madhya Pradesh (formerly Central Provinces and Berar), Madras, Orissa, Punjab (formerly East Punjab), Uttar Pradesh (formerly the United Provinces), and West Bengal (formerly part of Bengal Province).
- The eight Part B states were former princely states or groups of princely states, governed by a rajpramukh, who was usually the ruler of a constituent state, and an elected legislature. The rajpramukh was appointed by the President of India. The Part B states were Hyderabad, Jammu and Kashmir, Madhya Bharat, Mysore, Patiala and East Punjab States Union (PEPSU), Rajasthan, Saurashtra, and Travancore-Cochin.
- The ten Part C states included both the former chief commissioners' provinces and some princely states, and each was governed by a chief commissioner appointed by the President of India. The Part C states were Ajmer, Bhopal, Bilaspur, Coorg, Delhi, Himachal Pradesh, Cutch, Manipur, Tripura, and Vindhya Pradesh.
- The only Part D state was the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, which were administered by a lieutenant governor appointed by the central government.
States reorganization (1951–1956)[edit]
Original Maps Of Indiana
The Union Territory of Puducherry was created in 1954 comprising the previous French enclaves of Pondichéry, Karaikal, Yanam and Mahé.[13]Andhra State was created on 1 October 1953 from the Telugu-speaking northern districts of Madras State.[14]
The States Reorganisation Act of 1956 reorganised the states based on linguistic lines resulting in the creation of the new states.[15] As a result of this act, Madras State retained its name with Kanyakumari district added to form Travancore-Cochin. Andhra Pradesh was created with the merger of Andhra State with the Telugu-speaking districts of Hyderabad State in 1956. Kerala was created with the merger of Malabar district and the Kasaragod taluk of South Canara districts of Madras State with Travancore-Cochin. Mysore State was re-organized with the addition of districts of Bellary and South Canara (excluding Kasaragod taluk) and the Kollegal taluk of Coimbatore district from the Madras State, the districts of Belgaum, Bijapur, North Canara and Dharwad from Bombay State, the Kannada-majority districts of Bidar, Raichur and Gulbarga from Hyderabad State and the province of Coorg. The Laccadive Islands which were divided between South Canara and Malabar districts of Madras State were united and organised into the union territory of Lakshadweep.
Bombay State was enlarged by the addition of Saurashtra State and Kutch State, the Marathi-speaking districts of Nagpur Division of Madhya Pradesh and Marathwada region of Hyderabad State. Rajasthan and Punjab gained territories from Ajmer and Patiala and East Punjab States Union respectively and certain territories of Bihar was transferred to West Bengal.
Post-1956[edit]
Bombay State was split into the linguistic states of Gujarat and Maharashtra on 1 May 1960 by the Bombay Reorganisation Act.[16]Nagaland was formed on 1 December 1963.[17] The Punjab Reorganisation Act of 1966 resulted in the creation of Haryana on 1 November and the transfer of the northern districts of Punjab to Himachal Pradesh.[18] The act also designated Chandigarh as a union territory and the shared capital of Punjab and Haryana.[19][20]
Madras state was renamed Tamil Nadu in 1968. North-eastern states of Manipur, Meghalaya and Tripura were formed on 21 January 1972.[21] Mysore State was renamed as Karnataka in 1973. On 16 May 1975, Sikkim became the 22nd state of the Indian Union and the state's monarchy was abolished.[22] In 1987, Arunachal Pradesh and Mizoram became states on 20 February, followed by Goa on 30 May, while Goa's northern exclaves of Daman and Diu and Dadra and Nagar Haveli became separate union territories.[23]
In November 2000, three new states were created; namely, Chhattisgarh from eastern Madhya Pradesh, Uttaranchal from northwest Uttar Pradesh (renamed Uttarakhand in 2007) and Jharkhand from southern districts of Bihar.[24][25][26][27] Orissa was renamed as Odisha in 2011. Telangana was created on 2 June 2014 as ten former districts of north-western Andhra Pradesh.[28][29]
Current proposals[edit]
List[edit]
States[edit]
| State | ISO 3166-2:IN | Vehicle code | Zone | Capital | Largest city | Statehood | Population[30] | Area (km2) | Official languages[31] | Additional official languages[31] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andhra Pradesh | IN-AP | AP | Southern | Hyderabad(de jure) Amaravati(de facto)Note 1[32][33] | Visakhapatnam | 1 October 1953 | 49,506,799 | 160,205 | Telugu | — |
| Arunachal Pradesh | IN-AR | AR | North-Eastern | Itanagar | 20 February 1987 | 1,383,727 | 83,743 | English | — | |
| Assam | IN-AS | AS | North-Eastern | Dispur | Guwahati | 26 January 1950 | 31,205,576 | 78,550 | Assamese | Bengali |
| Bihar | IN-BR | BR | Eastern | Patna | 26 January 1950 | 104,099,452 | 94,163 | Hindi | Urdu | |
| Chhattisgarh | IN-CT | CG | Central | Raipur | 1 November 2000 | 25,545,198 | 135,194 | Hindi | — | |
| Goa | IN-GA | GA | Western | Panaji | Vasco da Gama | 30 May 1987 | 1,458,545 | 3,702 | Konkani | Marathi |
| Gujarat | IN-GJ | GJ | Western | Gandhinagar | Ahmedabad | 1 May 1960 | 60,439,692 | 196,024 | Gujarati | — |
| Haryana | IN-HR | HR | Northern | Chandigarh | Faridabad | 1 November 1966 | 25,351,462 | 44,212 | Hindi | Punjabi[34][35] |
| Himachal Pradesh | IN-HP | HP | Northern | Shimla(Summer) Dharamshala(Winter) | Shimla | 25 January 1971 | 6,864,602 | 55,673 | Hindi | English |
| Jammu and Kashmir | IN-JK | JK | Northern | Srinagar(Summer) Jammu(Winter) | Srinagar | 26 January 1950 | 12,541,302 | 222,236 101,387Note 2 | Urdu | — |
| Jharkhand | IN-JH | JH | Eastern | Ranchi | Jamshedpur | 15 November 2000 | 32,988,134 | 74,677 | Hindi | Urdu[36] |
| Karnataka | IN-KA | KA | Southern | Bengaluru | 1 November 1956 | 61,095,297 | 191,791 | Kannada | English | |
| Kerala | IN-KL | KL | Southern | Thiruvananthapuram | Kochi | 1 November 1956 | 33,406,061 | 38,863 | Malayalam | English |
| Madhya Pradesh | IN-MP | MP | Central | Bhopal | Indore | 1 November 1956 | 72,626,809 | 308,252 | Hindi | — |
| Maharashtra | IN-MH | MH | Western | Mumbai(Summer) Nagpur(Winter)[37] | Mumbai | 1 May 1960 | 112,374,333 | 307,713 | Marathi | — |
| Manipur | IN-MN | MN | North-Eastern | Imphal | 21 January 1972 | 2,855,794 | 22,347 | Meitei | English | |
| Meghalaya | IN-ML | ML | North-Eastern | Shillong | 21 January 1972 | 2,966,889 | 22,720 | English | Khasi[a] | |
| Mizoram | IN-MZ | MZ | North-Eastern | Aizawl | 20 February 1987 | 1,097,206 | 21,081 | English, Hindi, Mizo | — | |
| Nagaland | IN-NL | NL | North-Eastern | Kohima | Dimapur | 1 December 1963 | 1,978,502 | 16,579 | English | — |
| Odisha | IN-OR | OD | Eastern | Bhubaneswar | 26 January 1950 | 41,974,218 | 155,820 | Odia | — | |
| Punjab | IN-PB | PB | Northern | Chandigarh | Ludhiana | 1 November 1966 | 27,743,338 | 50,362 | Punjabi | — |
| Rajasthan | IN-RJ | RJ | Northern | Jaipur | 1 November 1956 | 68,548,437 | 342,269 | Hindi | English | |
| Sikkim | IN-SK | SK | North-Eastern | Gangtok | 16 May 1975 | 610,577 | 7,096 | Nepali, English | Bhutia, Gurung, Lepcha, Limbu, Manggar, Mukhia, Newari, Rai, Sherpa, Tamang | |
| Tamil Nadu | IN-TN | TN | Southern | Chennai | 26 January 1950 | 72,147,030 | 130,058 | Tamil | English | |
| Telangana | IN-TG | TS | Southern | HyderabadNote 1 | 2 June 2014 | 35,193,978[38] | 114,840[38] | Telugu, Urdu[39] | — | |
| Tripura | IN-TR | TR | North-Eastern | Agartala | 21 January 1972 | 3,673,917 | 10,492 | Bengali, English, Kokborok | — | |
| Uttar Pradesh | IN-UP | UP | Central | Lucknow | Kanpur | 26 January 1950 | 199,812,341 | 243,286 | Hindi | Urdu |
| Uttarakhand | IN-UT | UK | Central | DehradunNote 3 | 9 November 2000 | 10,086,292 | 53,483 | Hindi | Sanskrit[40] | |
| West Bengal | IN-WB | WB | Eastern | Kolkata | 26 January 1950 | 91,276,115 | 88,752 | Bengali, Nepali[b] | Hindi, Odia, Punjabi, Santali, and Urdu | |
- ^Note 1 Andhra Pradesh was divided into two states, Telangana and a residual Andhra Pradesh on 2 June 2014.[41][42][43]Hyderabad, located entirely within the borders of Telangana, is to serve as the capital for both states for a period of time not exceeding ten years.[44] The Government of Andhra Pradesh and the Andhra Pradesh Legislature completed the process of relocating to temporary facilities in the envisaged new capital city Amaravati in early 2017.[32]
- ^Note 2 The area of Jammu and Kashmir is 222,236 km2 according to Indian claims; thereof 101,387 km2 are under Indian administration
- ^Note 3 Dehradun is the interim capital of Uttarakhand. The town of Gairsain is envisaged as the state's new capital.
Union territories[edit]
| Union territory | ISO 3166-2:IN | Vehicle code | Capital | Largest city | Population[30] | Area (km2) | Official languages[31] | Additional official languages[31] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andaman and Nicobar Islands | IN-AN | AN | Port Blair | 380,581 | 8,249 | English, Hindi | — | |
| Chandigarh | IN-CH | CH | Chandigarh | —[c] | 1,055,450 | 114 | English | — |
| Dadra and Nagar Haveli | IN-DN | DN | Silvassa | 343,709 | 491 | Gujarati, Hindi | Marathi | |
| Daman and Diu | IN-DD | DD | Daman | 243,247 | 112 | English, Gujarati, Hindi, Konkani[d] | — | |
| Delhi | IN-DL | DL | New Delhi | —[e] | 16,787,941 | 1,490 | Hindi | Punjabi, Urdu[45] |
| Lakshadweep | IN-LD | LD | Kavaratti | 64,473 | 32 | Malayalam | English | |
| Puducherry | IN-PY | PY | Pondicherry | 1,247,953 | 492 | English,[46]Tamil | Malayalam, Telugu | |
Former states[edit]
| Map | State | Capital | Years | Successor state(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Madhya Bharat | Gwalior(winter) Indore(summer) | 1947–1956 | Madhya Pradesh | |
| Eastern States Union | Raipur | 1947–1948 | Bihar, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh | |
| Madras State | Madras | 1950–1969 | Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Karnataka | |
| Mysore State | Mysore | 1947–1973 | Karnataka | |
| Patiala and East Punjab States Union | Patiala | 1948–1956 | Punjab | |
| Bombay State | Bombay | 1947–1960 | Maharashtra, Gujarat | |
| Bhopal State | Bhopal | 1949–1956 | Madhya Pradesh | |
| Saurashtra | Rajkot | 1948–1956 | Bombay State | |
| Coorg State | Madikeri | 1950–1956 | Mysore State | |
| Travancore-Cochin | Trivandrum | 1949–1956 | Kerala, Madras State | |
| Hyderabad State | Hyderabad | 1948–1956 | Andhra Pradesh, Telangana (since 2014) and partially Maharashtra, North Karnataka | |
| Vindhya Pradesh | Rewa | 1948–1956 | Madhya Pradesh | |
| Kutch State | Bhuj | 1947–1956 | Bombay State | |
| Bilaspur State | Bilaspur | 1948–1954 | Himachal Pradesh | |
| Cooch Behar State | Cooch Behar | 1949 | West Bengal | |
| Ajmer State | Ajmer | 1947–1956 | Rajasthan |
See also[edit]
Notes[edit]
- ^Khasi language has been declared as the Additional Official Language for all purposes in the District, Sub-Division and Block level offices of the State Government located in the Districts of Khasi-Jaintia Hills of Meghalaya.
- ^Bengali and Nepali are the Official Languages in Darjeeling and Kurseong sub-divisions of Darjeeling district.
- ^Chandigarh is both a city and a union territory.
- ^It has also been informed that thecommunication with States/Centre has to be made in Hindi/English.
- ^Delhi is both a city and a union territory.
References[edit]
- ^'Article 73 broadly stated, provides that the executive power of the Union shall extend to the matters with respect to which Parliament has power to make laws. Article 162 similarly provides that the executive power of a State shall extend to the matters with respect to which the Legislature of a State has power to make laws. The Supreme Court has reiterated this position when it ruled in the Ramanaiah case that the executive power of the Union or of the State broadly speaking, is coextensive and coterminous with its respective legislative power.' Territoriality of executive powers of states in India, Balwant Singh Malik, Constitutional Law, 1998
- ^Krishna Reddy (2003). Indian History. New Delhi: Tata McGraw Hill. ISBN978-0-07-048369-9.
- ^Ramesh Chandra Majumdar (1977). Ancient India. Motilal Banarsidass Publishers. ISBN978-81-208-0436-4.
- ^Romila Thapar. A History of India: Part 1.
- ^G. Bongard-Levin. A History of India: Volume 1.
- ^Gupta Dynasty – MSN Encarta. Archived from the original on 1 November 2009.
- ^'India – Historical Setting – The Classical Age – Gupta and Harsha'. Historymedren.about.com. 2 November 2009. Retrieved 16 May 2010.
- ^Nilakanta Sastri, K.A. (2002) [1955]. A history of South India from prehistoric times to the fall of Vijayanagar. New Delhi: Indian Branch, Oxford University Press. p. 239. ISBN978-0-19-560686-7.
- ^Chandra, Satish. Medieval India: From Sultanate To The Mughals. p. 202.
- ^'Regional states, c. 1700–1850'. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
- ^Grewal, J. S. (1990). 'Chapter 6: The Sikh empire (1799–1849)'. The Sikh empire (1799–1849). The New Cambridge History of India. The Sikhs of the Punjab. Cambridge University Press.
- ^'Article 1'. Constitution of India. Archived from the original on 2 April 2012.
- ^'Reorganisation of states'(PDF). Economic Weekly. Retrieved 31 December 2015.
- ^'Map of Madras Presidency in 1909'. 28 March 2011. Retrieved 15 October 2013.
- ^'Article 1'. Constitution of India. Law Ministry, GOI. Archived from the original on 2 April 2012. Retrieved 31 December 2015.
- ^J.C. Aggarwal, S.P. Agrawal (1995). Uttarakhand: Past, Present, and Future. New DElhi: Concept Publishing. pp. 89–90.
- ^'Nagaland History & Geography-Source'. india.gov.in. Retrieved 17 June 2013.
- ^'Himachal Pradesh Tenth Five Year Plan'(PDF). Retrieved 17 June 2013.
- ^'The Punjab Reorganisation Act 1966'(PDF). india.gov.in. Retrieved 17 June 2013.
- ^'State map of India'. Travel India guide. Retrieved 17 June 2013.
- ^'Snapshot of North Eastern States'(PDF). thaibicindia.in. Archived from the original(PDF) on 22 December 2009. Retrieved 17 February 2016.
- ^'About Sikkim'. Official website of the Government of Sikkim. Archived from the original on 25 May 2009. Retrieved 15 June 2009.
- ^'Goa Chronology'. goaonline.in. Archived from the original on 21 July 2011. Retrieved 17 February 2016.
- ^'Official Website of Government of Jharkhand'. Jharkhand.gov.in. Archived from the original on 21 June 2013. Retrieved 17 June 2013.
- ^'Chhattisgarh state – History'. Cg.gov.in. Archived from the original on 4 July 2010. Retrieved 17 June 2013.
- ^Chopra, Jasi Kiran (2 January 2007). 'Uttaranchal is Uttarakhand, BJP cries foul'. Times of India. Retrieved 22 January 2013.
- ^'About Us: Uttarakhand Government Portal, India'. Uk.gov.in. 9 November 2000. Retrieved 17 June 2013.
- ^'The Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act, 2014'(PDF). Ministry of law and justice, Government of India. Archived from the original(PDF) on 8 January 2016. Retrieved 3 March 2014.
- ^'Telangana bill passed by upper house'. The Times of India. Retrieved 20 February 2014.
- ^ ab'List of states with Population, Sex Ratio and Literacy Census 2011'.
- ^ abcd'Report of the Commissioner for linguistic minorities: 50th report (July 2012 to June 2013)'(PDF). Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities, Ministry of Minority Affairs, Government of India. Archived from the original(pdf) on 8 July 2016. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- ^ ab'After 2200 Years, Amaravati Gets Back Power!'.
- ^'Data'. ap.gov.in. Archived from the original on 3 August 2017. Retrieved 27 June 2014.
- ^'Haryana grants second language status to Punjabi'. Hindustan Times. 28 January 2010.
- ^'Punjabi gets second language status in Haryana'. Zee news. 28 January 2010.
- ^'Research data'. ierj.in.
- ^Monsoon session to start in Maha’s winter Capital Nagpur from July 4
- ^ ab'Telangana State Profile'(PDF). Telangana government portal. p. 34. Retrieved 11 June 2014.
- ^'Urdu Gets First Language Status'.
- ^'Sanskrit: Reviving the language in today's India – Livemint'.
- ^'Bifurcated into Telangana State and residual Andhra Pradesh State'. The Times of India. 2 June 2014.
- ^'The Gazette of India : The Andhra Pradesh Reorganization Act, 2014'(PDF). Ministry of Law and Justice. Government of India. 1 March 2014. Retrieved 23 April 2014.[permanent dead link]
- ^'The Gazette of India : The Andhra Pradesh Reorganization Act, 2014 Sub-section'(PDF). 4 March 2014. Retrieved 23 April 2014.
- ^Sanchari Bhattacharya (1 June 2014). 'Andhra Pradesh Minus Telangana: 10 Facts'. NDTV.
- ^'Official Language Act 2000'(PDF). Government of Delhi. 2 July 2003. Retrieved 17 July 2015.
- ^'Regional data'(PDF). lawsofindia.org.